Textbook Question
The smectic liquid crystalline phase can be said to be more highly ordered than the nematic phase. In what sense is this true?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
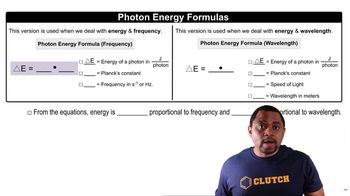
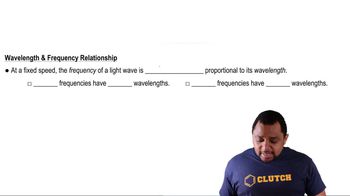

If you want to dope GaAs to make an n-type semiconductor with an element to replace Ga, which element(s) would you pick?
Cadmium telluride is an important material for solar cells. (d) With respect to silicon, does CdTe absorb a larger or smaller portion of the solar spectrum?