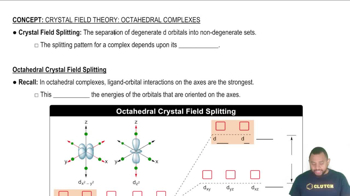
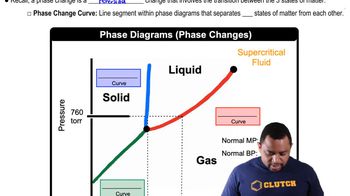
Textbook Question
The phase diagram of a hypothetical substance is
(b) What is the physical state of the substance under the following conditions? (i) T = 150 K, P = 0.2 atm; (ii) T = 100 K, P = 0.8 atm; (iii) T = 300K, P = 1.0atm. [Section 11.6]
1
views