Gaseous iodine pentafluoride, IF5, can be prepared by the reaction of solid iodine and gaseous fluorine: I2(s) + 5 F2(g) → 2 IF5(g) A 5.00-L flask containing 10.0 g of I2 is charged with 10.0 g of F2, and the reaction proceeds until one of the reagents is completely consumed. After the reaction is complete, the temperature in the flask is 125 °C. (a) What is the partial pressure of IF5 in the flask?

Natural gas is very abundant in many Middle Eastern oil fields. However, the costs of shipping the gas to markets in other parts of the world are high because it is necessary to liquefy the gas, which is mainly methane and has a boiling point at atmospheric pressure of -164 °C. One possible strategy is to oxidize the methane to methanol, CH3OH, which has a boiling point of 65 °C and can therefore be shipped more readily. Suppose that 3.03×108 m3 of methane at atmospheric pressure and 25 °C is oxidized to methanol. (a) What volume of methanol is formed if the density of CH3OH is 0.791 g/mL?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Stoichiometry

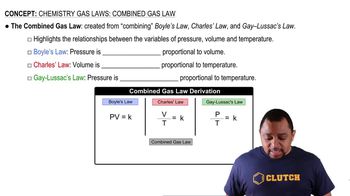
Gas Laws
Density and Volume Conversion

Gaseous iodine pentafluoride, IF5, can be prepared by the reaction of solid iodine and gaseous fluorine: I2(s) + 5 F2(g) → 2 IF5(g) A 5.00-L flask containing 10.0 g of I2 is charged with 10.0 g of F2, and the reaction proceeds until one of the reagents is completely consumed. After the reaction is complete, the temperature in the flask is 125 °C. (b) What is the mole fraction of IF5 in the flask?
Gaseous iodine pentafluoride, IF5, can be prepared by the reaction of solid iodine and gaseous fluorine: I2(s) + 5 F2(g) → 2 IF5(g) A 5.00-L flask containing 10.0 g of I2 is charged with 10.0 g of F2, and the reaction proceeds until one of the reagents is completely consumed. After the reaction is complete, the temperature in the flask is 125 °C. (c) Draw the Lewis structure of IF5.
