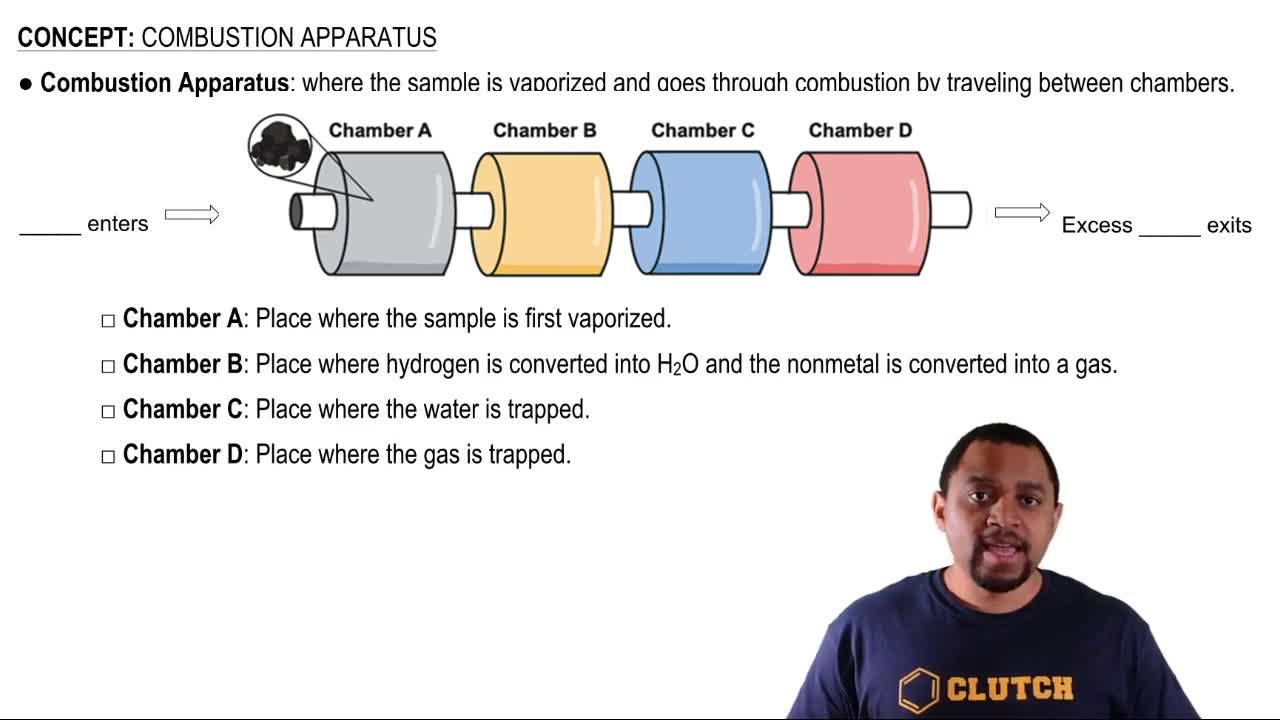
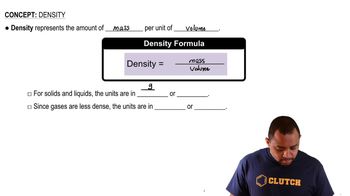
Ammonia and hydrogen chloride react to form solid ammonium chloride: NH3(g) + HCl(g) → NH4Cl(s)
Two 2.00-L flasks at 25 °C are connected by a valve, as shown in the drawing. One flask contains 5.00 g of NH3(g), and the other contains 5.00 g of HCl(g). When the valve is opened, the gases react until one is completely consumed. (b) What will be the final pressure of the system after the reaction is complete? (Neglect the volume of the ammonium chloride formed.)