
During a person's typical breathing cycle, the CO2 concentration in the expired air rises to a peak of 4.6% by volume.(a) Calculate the partial pressure of the CO2 in the expiredair at its peak, assuming 1 atm pressure and a body temperature of 37 °C.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Partial Pressure

Gas Laws
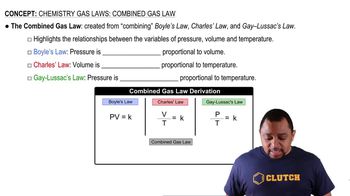
Body Temperature and Gas Behavior

Both Jacques Charles and Joseph Louis Guy-Lussac were avid balloonists. In his original flight in 1783, Jacques Charles used a balloon that contained approximately 31,150 L of H2. He generated the H2 using the reaction between iron and hydrochloric acid: Fe1s2 + 2 HCl1aq2 ¡ FeCl21aq2 + H21g2 How many kilograms of iron were needed to produce this volume of H2 if the temperature was 22 °C?
Consider the apparatus shown in the following drawing. (a) When the valve between the two containers is opened and the gases are allowed to mix, how does the volume occupied by the N2 gas change?
Consider the apparatus shown in the following drawing. (a) When the valve between the two containers is opened and the gases are allowed to mix, what is the partial pressure of N2 after mixing?
