Both Jacques Charles and Joseph Louis Guy-Lussac were avid balloonists. In his original flight in 1783, Jacques Charles used a balloon that contained approximately 31,150 L of H2. He generated the H2 using the reaction between iron and hydrochloric acid: Fe1s2 + 2 HCl1aq2 ¡ FeCl21aq2 + H21g2 How many kilograms of iron were needed to produce this volume of H2 if the temperature was 22 °C?
Ch.10 - Gases

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 10, Problem 60
Acetylene gas, C2H21g2, can be prepared by the reaction ofcalcium carbide with water:CaC21s2 + 2 H2O1l2¡Ca1OH221aq2 + C2H21g2Calculate the volume of C2H2 that is collected over water at23 °C by reaction of 1.524 g of CaC2 if the total pressure ofthe gas is 100.4 kPa. (The vapor pressure of water is tabulatedin Appendix B.)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the balanced chemical equation for the reaction: \( \text{CaC}_2 (s) + 2 \text{H}_2\text{O} (l) \rightarrow \text{Ca(OH)}_2 (aq) + \text{C}_2\text{H}_2 (g) \).
Calculate the moles of \( \text{CaC}_2 \) using its molar mass: \( \text{moles of CaC}_2 = \frac{\text{mass of CaC}_2}{\text{molar mass of CaC}_2} \).
Use stoichiometry to find the moles of \( \text{C}_2\text{H}_2 \) produced, knowing that 1 mole of \( \text{CaC}_2 \) produces 1 mole of \( \text{C}_2\text{H}_2 \).
Determine the partial pressure of \( \text{C}_2\text{H}_2 \) by subtracting the vapor pressure of water from the total pressure: \( P_{\text{C}_2\text{H}_2} = P_{\text{total}} - P_{\text{H}_2\text{O}} \).
Use the ideal gas law \( PV = nRT \) to calculate the volume of \( \text{C}_2\text{H}_2 \), where \( P \) is the partial pressure of \( \text{C}_2\text{H}_2 \), \( n \) is the moles of \( \text{C}_2\text{H}_2 \), \( R \) is the ideal gas constant, and \( T \) is the temperature in Kelvin.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
7mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is the calculation of reactants and products in chemical reactions based on the balanced chemical equation. It allows us to determine the amount of product formed from a given amount of reactant. In this case, understanding the stoichiometric relationship between calcium carbide (CaC2) and acetylene (C2H2) is essential to calculate the volume of gas produced from the mass of CaC2 used.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Stoichiometry Concept
Gas Laws
Gas laws describe the behavior of gases in relation to pressure, volume, and temperature. The Ideal Gas Law (PV=nRT) is particularly useful for calculating the volume of a gas under specific conditions. In this problem, we need to apply the gas laws to find the volume of acetylene gas produced, taking into account the total pressure and the vapor pressure of water at the given temperature.
Recommended video:
Guided course
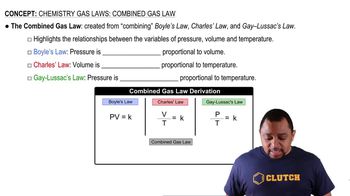
Combined Gas Law
Vapor Pressure of Water
The vapor pressure of water is the pressure exerted by water vapor in equilibrium with its liquid at a given temperature. It is crucial to consider this when collecting gases over water, as the total pressure measured includes both the pressure of the gas and the vapor pressure of water. To find the pressure of the acetylene gas alone, we must subtract the vapor pressure of water from the total pressure.
Recommended video:
Guided course
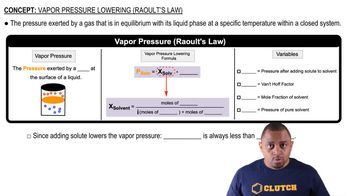
Raoult's Law and Vapor Pressure
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
During a person's typical breathing cycle, the CO2 concentration in the expired air rises to a peak of 4.6% by volume.(a) Calculate the partial pressure of the CO2 in the expiredair at its peak, assuming 1 atm pressure and a body temperature of 37 °C.
Textbook Question
Consider the apparatus shown in the following drawing. (a) When the valve between the two containers is opened and the gases are allowed to mix, how does the volume occupied by the N2 gas change?
Textbook Question
Consider the apparatus shown in the following drawing. (a) When the valve between the two containers is opened and the gases are allowed to mix, what is the partial pressure of N2 after mixing?
Textbook Question
Consider a mixture of two gases, A and B, confined in a closed vessel. A quantity of a third gas, C, is added to the same vessel at the same temperature. How does the addition of gas C affect the following: (a) the partial pressure of gas A?
