(a) Based on the lattice energies of MgCl2 and SrCl2 given in Table 8.1, what is the range of values that you would expect for the lattice energy of CaCl2?

(b) A substance, XY, formed from two different elements, melts at −33 °C. Is XY likely to be a covalent or an ionic substance?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Covalent vs. Ionic Bonds

Melting Point as an Indicator
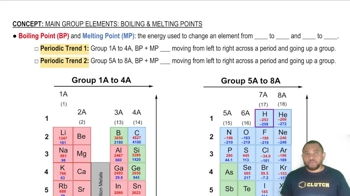
Properties of Molecular Compounds

(b) Using data from Appendix C, Figure 7.11, Figure 7.13, and the value of the second ionization energy for Ca, 1145 kJ/mol, calculate the lattice energy of CaCl2.
(a) State whether or not the bonding in each substance is likely to be covalent: (i) glucose, (ii) nitrogen, (iii) aluminum hydroxide, (iv) ammonia, (v) neon.
Using Lewis symbols and Lewis structures, make a sketch of the formation of NCl3 from N and Cl atoms, showing valence-shell electrons. (a) How many valence electrons does N have initially? (c) How many valence electrons surround the N in the NCl3 molecule? (d) How many valence electrons surround each Cl in the NCl3 molecule?
Using Lewis symbols and Lewis structures, make a sketch of the formation of NCl3 from N and Cl atoms, showing valence-shell electrons. (b) How many bonds Cl has to make in order to achieve an octet?
