A number of salts containing the tetrahedral polyatomic anion, BF4-, are ionic liquids, whereas salts containing the somewhat larger tetrahedral ion SO42- do not form ionic liquids. Explain this observation.

(c) Why do substances with high surface tension also tend to have high viscosities?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Surface Tension
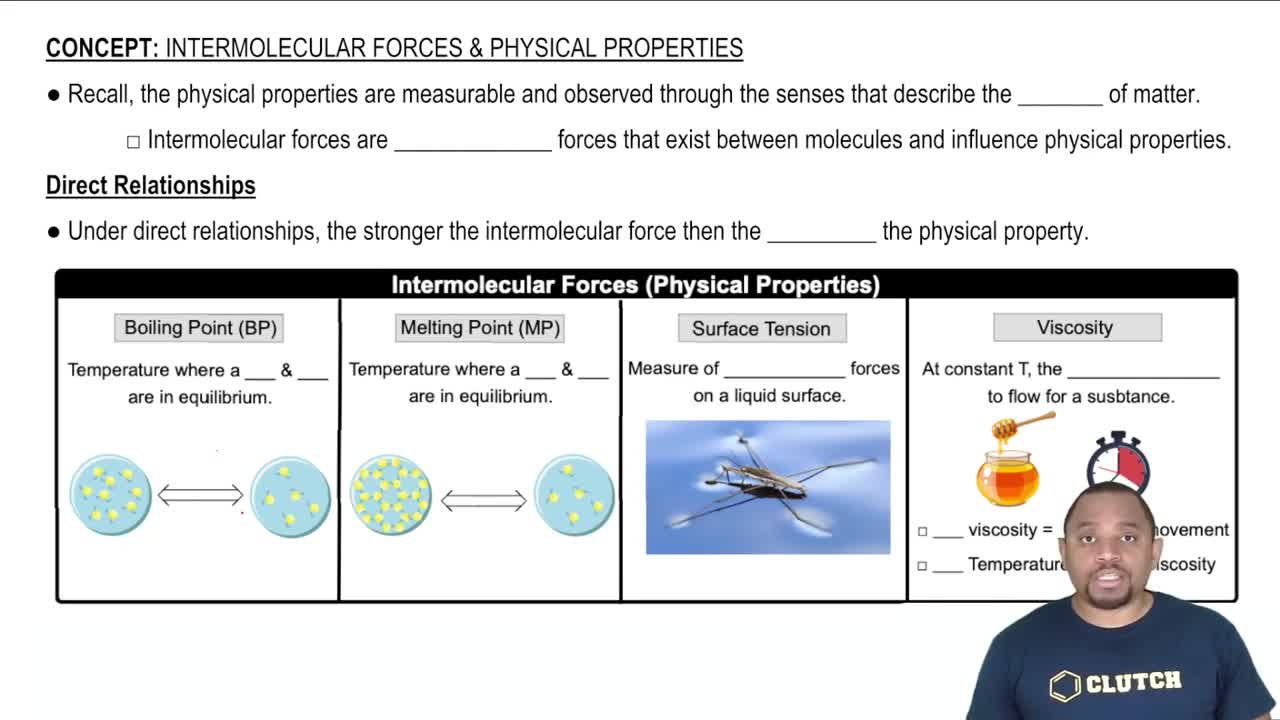
Viscosity

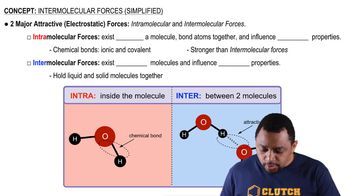
Intermolecular Forces
The generic structural formula for a 1-alkyl-3-methylimid- azolium cation is where R is a -CH2(CH2)nCH3 alkyl group. The melting points of the salts that form between 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium cation and the PF6- anion are as follows: R = CH2CH3 (m.p. = 60 °C), R = CH2CH2CH3 (m.p. = 40 °C), r = CH2CH2CH2CH3 (m.p. = 10 °C), and R = CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 (m.p. = -61 °C). Why does the melting point decrease as the length of alkyl group increases?
(b) What is the relationship between viscosity and temperature?
Based on their composition and structure, list CH2Cl2, CH3CH2CH3, and CH3CH2OH in order of (a) increasing intermolecular forces (c) increasing surface tension
Liquids can interact with flat surfaces just as they can with capillary tubes; the cohesive forces within the liquid can be stronger or weaker than the adhesive forces between liquid and surface:
(b) Which of these diagrams, i or ii, rep- resents what happens when water is on a nonpolar surface?
