In what forms is oxygen commonly found in nature?

Compare some of the physical properties of H2S, NaH, and PdHx.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Molecular Structure and Polarity

Ionic vs. Covalent Compounds

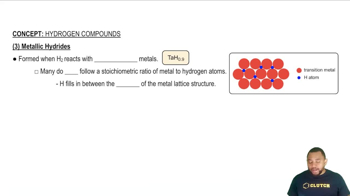
Metal-Hydride Properties
Explain why the properties of boron differ so markedly from the properties of the other group 3A elements.
Describe the structures of the white and red allotropes of phosphorus, and explain why white phosphorus is so reactive.
Which of the group 4A elements have allotropes with the diamond structure? Which have metallic allotropes? How does the variation in the structure of the group 4A elements illustrate how metallic character varies down a periodic group?
GeCl4 reacts with Cl- to give GeCl62-, but CCl4 does not react with excess Cl-. Explain.
Using the shorthand notation of Figure 22.9, draw the structure of the cyclic silicate anion in which four SiO4 tetrahedra share O atoms to form an eight-membered ring of alternating Si and O atoms. Give the formula and charge of the anion.
