When a mixture of 10.0 g of acetylene (C2H2) and 10.0 g of oxygen (O2) is ignited, the resulting combustion reaction produces CO2 and H2O. (c) How many grams of CO2 and H2O are present after the reaction is complete?
Ch.3 - Chemical Reactions and Reaction Stoichiometry

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 3, Problem 107
Viridicatumtoxin B, C30H31NO10, is a natural antibiotic compound. It requires a synthesis of 12 steps in the laboratory. Assuming all steps have equivalent yields of 85%, which is the final percent yield of the total synthesis?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify that the problem involves calculating the overall percent yield of a multi-step synthesis, where each step has an equivalent yield of 85%.
Recall that the overall yield of a multi-step process is the product of the yields of each individual step.
Express the yield of each step as a decimal: 85% becomes 0.85.
Since there are 12 steps, raise the yield of one step to the power of 12: \((0.85)^{12}\).
Convert the result back to a percentage by multiplying by 100 to find the final percent yield of the total synthesis.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
51sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Percent Yield
Percent yield is a measure of the efficiency of a chemical reaction, calculated as the ratio of the actual yield to the theoretical yield, multiplied by 100. It indicates how much product is obtained from a reaction compared to the maximum possible amount, helping chemists assess the effectiveness of their synthetic processes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Percent Yield in Reactions
Sequential Reactions
In synthetic chemistry, sequential reactions refer to a series of chemical transformations where the product of one reaction serves as the reactant for the next. Each step can affect the overall yield, as the final product yield is influenced by the yields of all preceding steps, necessitating careful calculation of cumulative effects.
Recommended video:
Guided course
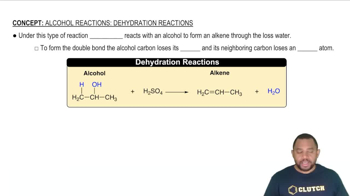
Alcohol Reactions: Dehydration Reactions
Multiplicative Yield Calculation
When dealing with multiple steps in a synthesis, the overall yield is calculated by multiplying the yields of each individual step. For example, if each step has a yield of 85%, the final yield is determined by raising the yield to the power of the number of steps, reflecting the compounding effect of losses at each stage.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Percent Yield in Reactions
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
When a mixture of 10.0 g of acetylene (C2H2) and 10.0 g of oxygen (O2) is ignited, the resulting combustion reaction produces CO2 and H2O. (c) How many grams of C2H2 are present after the reaction is complete?
Textbook Question
(b) Because atoms are spherical, they cannot occupy all of the space of the cube. The silver atoms pack in the solid in such a way that 74% of the volume of the solid is actually filled with the silver atoms. Calculate the volume of a single silver atom.
Textbook Question
Burning acetylene in oxygen can produce three different carbon-containing products: soot (very fine particles of graphite), CO(g), and CO2(g). (c) Why, when the oxygen supply is adequate, is CO2(g) the predominant carbon-containing product of the combustion of acetylene?
