Textbook Question
Consider the following XF4 ions: PF4-, BrF4-, ClF4+, and AlF4-. (a) Which of the ions have more than an octet of electrons around the central atom?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Consider the following XF4 ions: PF4-, BrF4-, ClF4+, and AlF4-. (a) Which of the ions have more than an octet of electrons around the central atom?
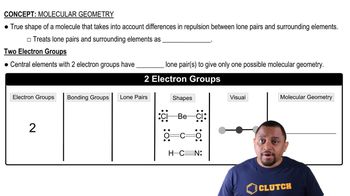
Consider the following XF4 ions: PF4-, BrF4-, ClF4+, and AlF4-. (c) Which of the ions will have an octahedral electron-domain geometry?
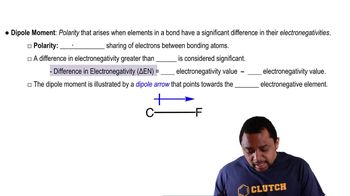
a. Does SCl2 have a nonzero dipole moment?
(b) It turns out that ozone, O3, has a small dipole moment. How is this possible, given that all the atoms are the same?