Textbook Question
(a) What is a catalyst? (b) What is the difference between a homogeneous and a heterogeneous catalyst?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
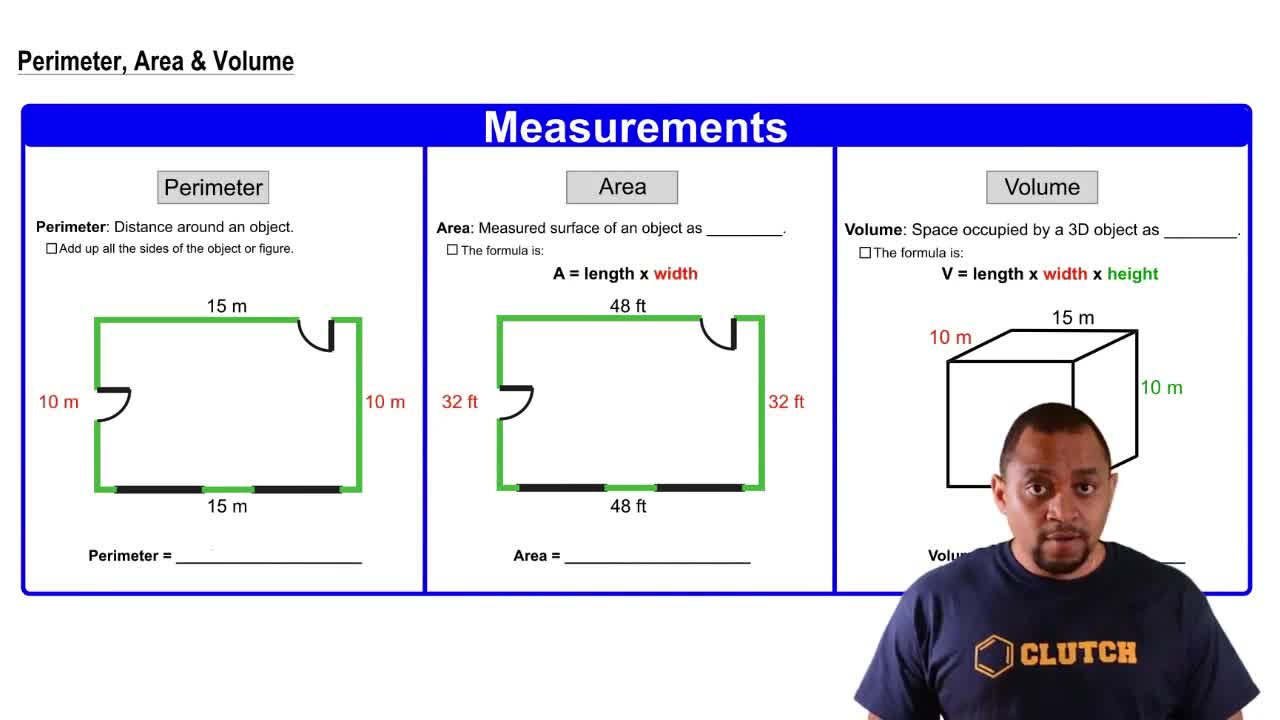

(a) What is a catalyst? (b) What is the difference between a homogeneous and a heterogeneous catalyst?
(c) Do catalysts affect the overall enthalpy change for a reaction, the activation energy, or both?
The addition of NO accelerates the decomposition of N2O, possibly by the following mechanism: NO1g2 + N2O1g2¡N21g2 + NO21g2 2 NO21g2¡2 NO1g2 + O21g2 (b) Is NO serving as a catalyst or an intermediate in this reaction?