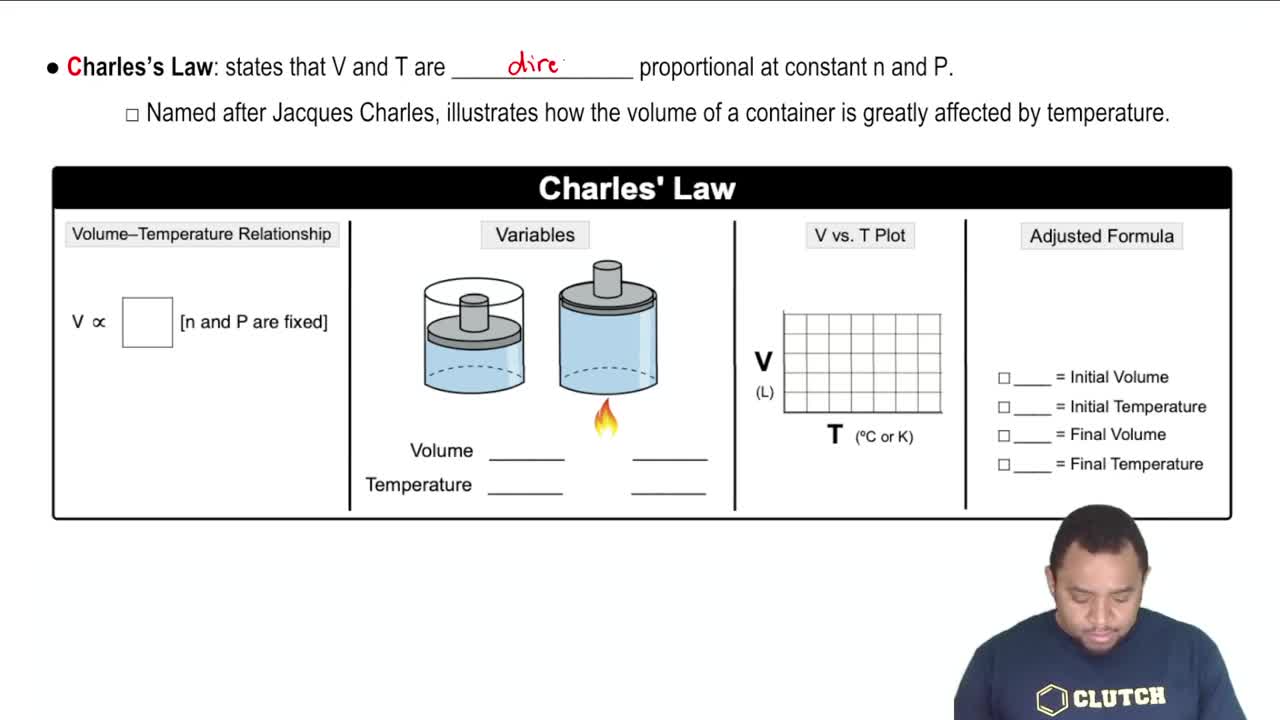
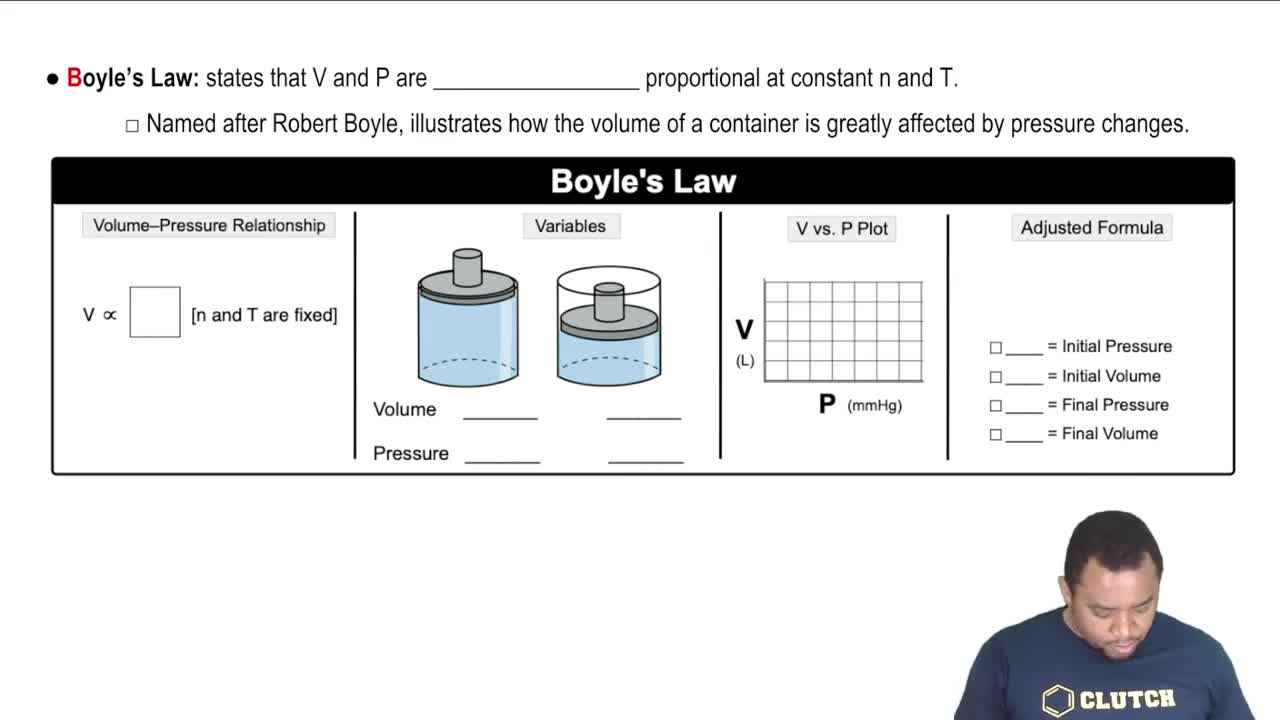
Textbook Question
Which gas sample has the greatest pressure? Assume that all the samples are at the same temperature. Explain.


 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Which gas sample has the greatest pressure? Assume that all the samples are at the same temperature. Explain.
Aerosol cans carry clear warnings against incineration because of the high pressures that can develop upon heating. Suppose that a can contains a residual amount of gas at a pressure of 755 mmHg and a temperature of 25 °C. What would the pressure be if the can were heated to 1155 °C?
A sample of nitrogen gas in a 1.75-L container exerts a pressure of 1.35 atm at 25 °C. What is the pressure if the volume of the container is maintained constant and the temperature is raised to 355 °C?
Use the molar volume of a gas at STP to determine the volume (in L) occupied by 33.6 g of neon at STP.