Which gas sample has the greatest pressure? Assume that all the samples are at the same temperature. Explain.
Ch.5 - Gases

Chapter 5, Problem 51
Aerosol cans carry clear warnings against incineration because of the high pressures that can develop upon heating. Suppose that a can contains a residual amount of gas at a pressure of 755 mmHg and a temperature of 25 °C. What would the pressure be if the can were heated to 1155 °C?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the initial and final conditions of the gas: initial pressure \( P_1 = 755 \text{ mmHg} \), initial temperature \( T_1 = 25 \degree C \), and final temperature \( T_2 = 1155 \degree C \).
Convert the temperatures from Celsius to Kelvin using the formula \( T(K) = T(\degree C) + 273.15 \).
Apply Gay-Lussac's Law, which states that \( \frac{P_1}{T_1} = \frac{P_2}{T_2} \), where \( P_2 \) is the final pressure we want to find.
Rearrange the equation to solve for \( P_2 \): \( P_2 = P_1 \times \frac{T_2}{T_1} \).
Substitute the known values into the equation to calculate \( P_2 \).

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Gas Laws
Gas laws describe the behavior of gases in relation to pressure, volume, and temperature. The most relevant here is the Ideal Gas Law, which states that for a given amount of gas, the pressure is directly proportional to the temperature when volume is constant. This relationship is crucial for predicting how the pressure in the aerosol can will change as the temperature increases.
Recommended video:
Guided course
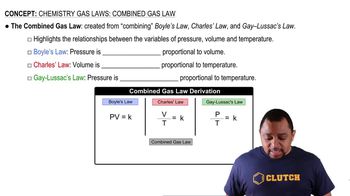
Combined Gas Law
Charles's Law
Charles's Law specifically states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature when pressure is held constant. Although the volume of the aerosol can does not change, understanding this law helps in grasping how temperature affects pressure. In this scenario, as the temperature rises, the pressure inside the can will also increase significantly.
Recommended video:
Guided course
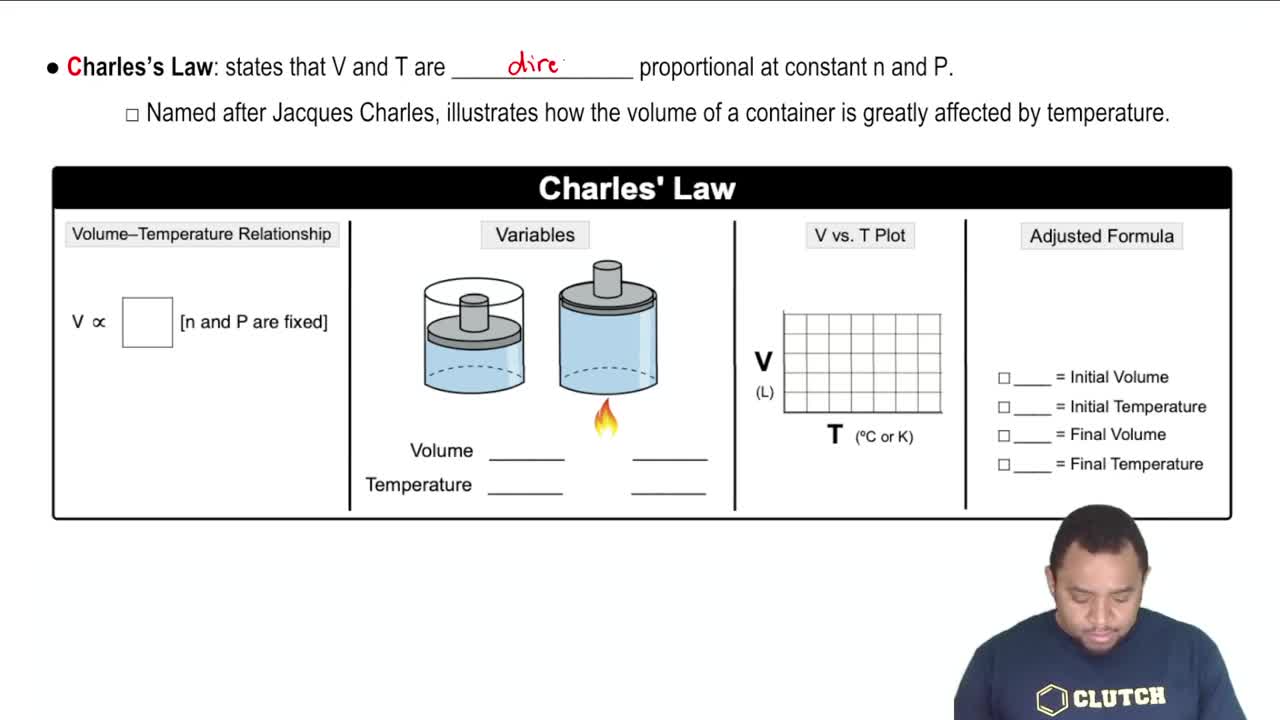
Charles's Law
Absolute Temperature
Absolute temperature is measured in Kelvin and is essential for gas law calculations. To convert Celsius to Kelvin, you add 273.15. This conversion is necessary because gas laws require temperature to be in absolute terms to accurately predict changes in pressure and volume, ensuring that calculations reflect the true kinetic energy of gas particles.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Temperature vs Heat
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
This picture represents a sample of gas at a pressure of 1 atm, a volume of 1 L, and a temperature of 25 °C. Draw a similar picture showing what would happen to the sample if the volume were reduced to 0.5 L and the temperature were increased to 250 °C. What would happen to the pressure?
Textbook Question
A sample of nitrogen gas in a 1.75-L container exerts a pressure of 1.35 atm at 25 °C. What is the pressure if the volume of the container is maintained constant and the temperature is raised to 355 °C?
Textbook Question
Use the molar volume of a gas at STP to determine the volume (in L) occupied by 33.6 g of neon at STP.
Textbook Question
Use the molar volume of a gas at STP to calculate the density (in g/L) of nitrogen gas at STP.
