A cube of gold that is 1.00 cm on a side has a mass of 19.3 g. A single gold atom has a mass of 197.0 u. (b) From the information given, estimate the diameter in Å of a single gold atom.

"The diameter of a rubidium atom is 495 pm We will consider two different ways of placing the atoms on a surface. In arrangement A, all the atoms are lined up with one another to form a square grid. Arrangement B is called a close-packed arrangement because the atoms sit in the 'depressions' formed by the previous row of atoms:

(c) If extended to three dimensions, which arrangement would lead to a greater density for Rb metal?"
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
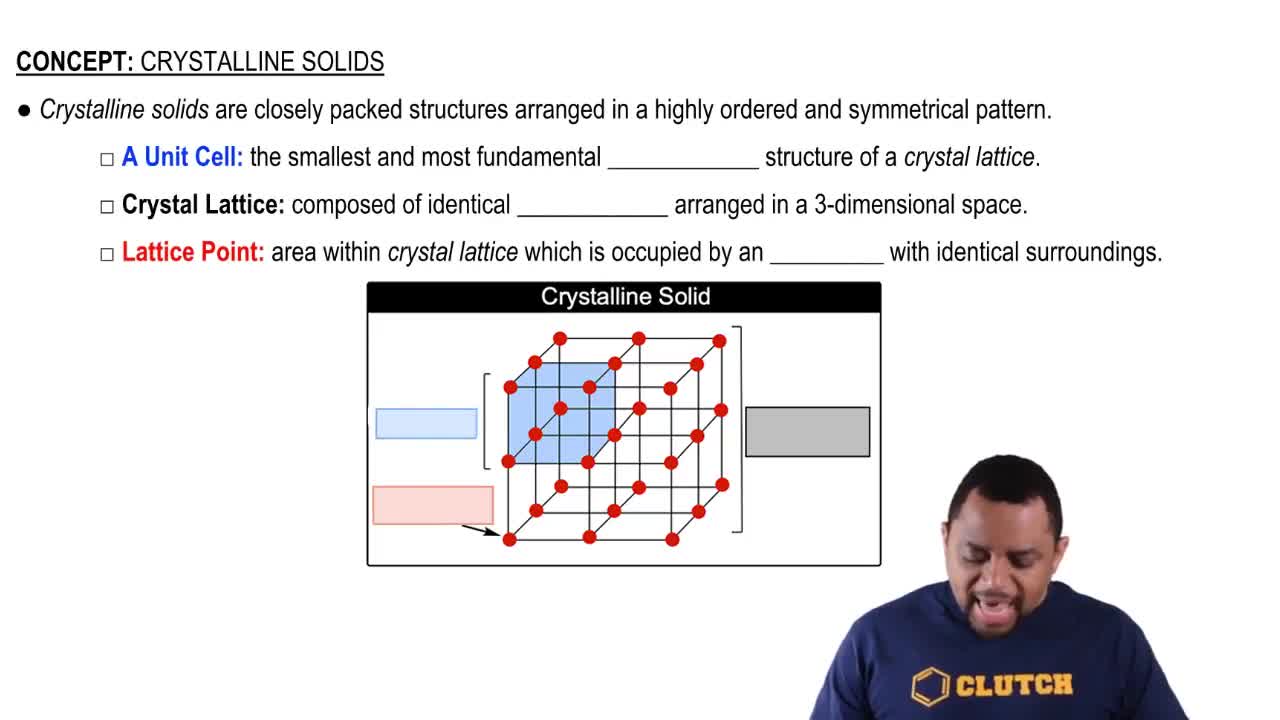
Atomic Arrangement

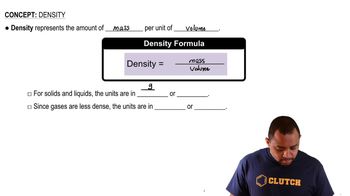
Density
Close-Packing
The diameter of a rubidium atom is 495 pm We will consider two different ways of placing the atoms on a surface. In arrangement A, all the atoms are lined up with one another to form a square grid. Arrangement B is called a close-packed arrangement because the atoms sit in the 'depressions' formed by the previous row of atoms: (a) Using arrangement A, how many Rb atoms could be placed on a square surface that is 1.0 cm on a side?
(b) How many molecules of C13H18O2 are in this tablet?
"The diameter of a rubidium atom is 495 pm We will consider two different ways of placing the atoms on a surface. In arrangement A, all the atoms are lined up with one another to form a square grid. Arrangement B is called a close-packed arrangement because the atoms sit in the 'depressions' formed by the previous row of atoms:
(c) By what factor has the number of atoms on the surface increased in going to arrangement B from arrangement A?
(a) Assuming the dimensions of the nucleus and atom shown in Figure 2.10, what fraction of the volume of the atom is taken up by the nucleus?
