Textbook Question
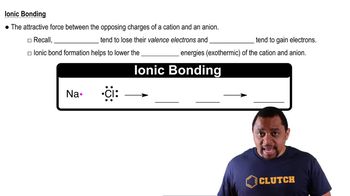
A sodium ion, Na+, with a charge of 1.6⨉10-19 C and a chloride ion, Cl - , with charge of -1.6⨉10-19 C, are separated by a distance of 0.50 nm. How much work would be required to increase the separation of the two ions to an infinite distance?