Textbook Question
Name each ether. a.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
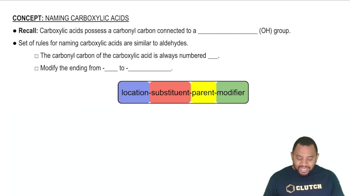
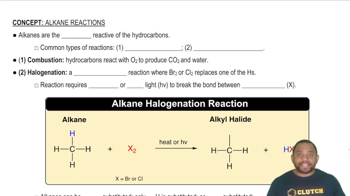
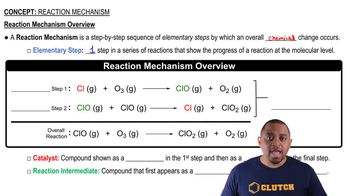
Name each ether. a.
Determine the products of each carboxylic acid reaction. a.
Determine the products of each carboxylic acid reaction. b.
Determine the products of each carboxylic acid reaction. a.
Name each ether. b.
Name each ether. c.