In acidic aqueous solution, the complex trans-[Co(en)2Cl1]2+(aq) undergoes the following substitution reaction:
trans-[Co(en)2Cl1]+(aq) + H2O(l) → trans-[Co(en)2(H2O)Cl]2+(aq) + Cl–(aq)
The reaction is first order in trans-[Co(en)2Cl2]+(aq), and the rate constant at 25°C is 3.2×10–5 s–1.
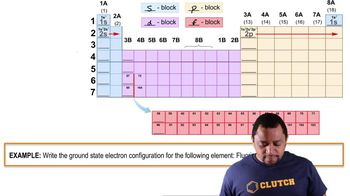
e. Draw a crystal field energy-level diagram for trans-[Co(en)2Cl2]+ that takes account of the fact that Cl– is a weaker-field ligand than ethylenediamine.