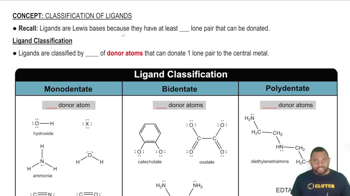
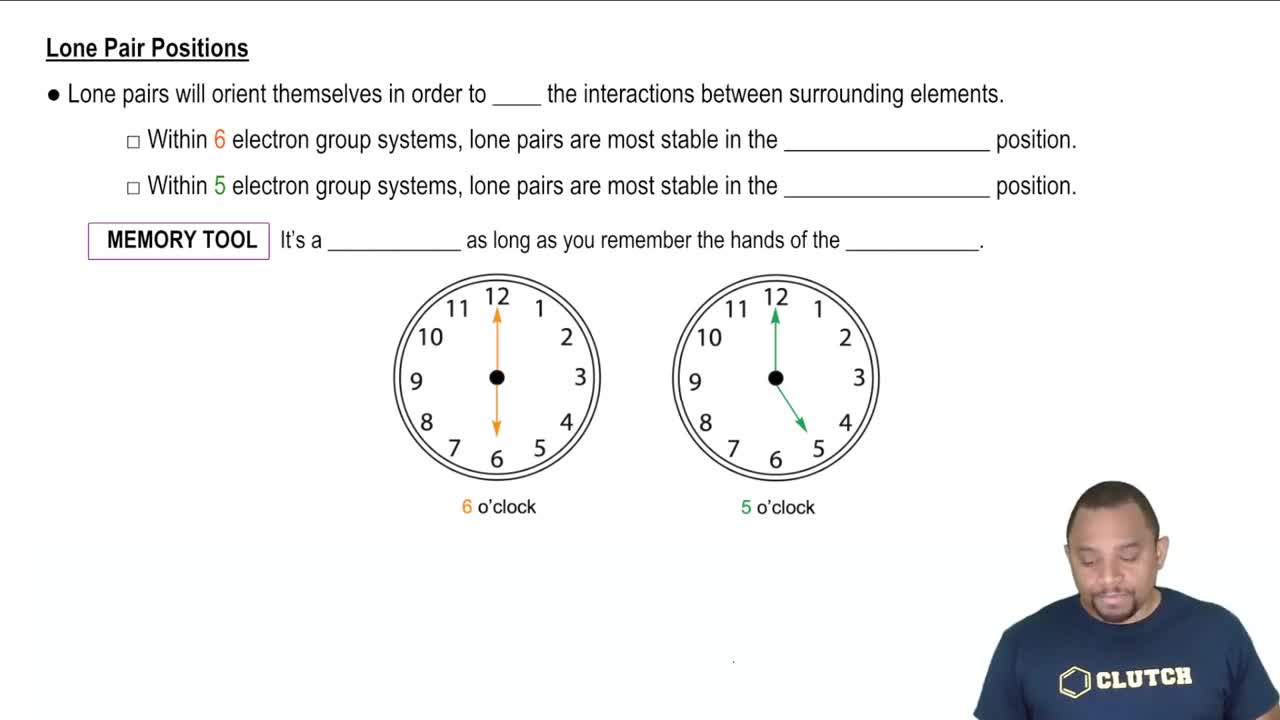
Consider the six second- and third-row elements in groups 4A–6A of the periodic table:
Possible structures for the binary fluorides of each of these elements in its highest oxidation state are shown below.
(b) Explain why the fluorides of nitrogen and phosphorus have different molecular structures but the fluorides of carbon and silicon have the same molecular structure.