Textbook Question
Consider the elements N, Si, Al, S, and F. Identify which of these elements:
c. Is a semiconductor

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

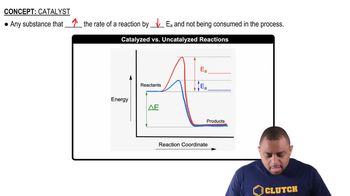

Consider the elements N, Si, Al, S, and F. Identify which of these elements:
c. Is a semiconductor
Which compound in each of the following pairs is more ionic?
(d) BCl3 or AlCl3
Give one example from main-group chemistry that illustrates each of the following descriptions.
d. Polar molecule that violates the octet rule
Consider the elements C, Se, B, Sn, and Cl. Identify which of these elements:
e. Forms a hydride with the empirical formula
Look at the location of elements A, B, C, and D in the following periodic table:
(e) Which of these oxides has the highest melting point? Which has the lowest melting point?
Locate each of the following elements on the periodic table.
(f) Group 5A element that forms the strongest p bonds