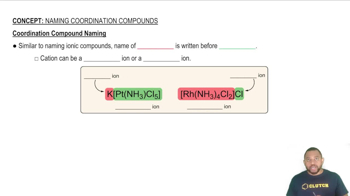
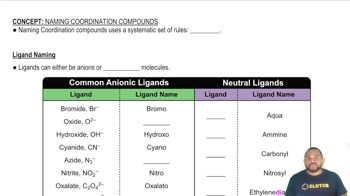
Cobalt(III) trifluoroacetylacetonate, Co(tfac)3, is a sixcoordinate, octahedral metal chelate in which three planar, bidentate tfac ligands are attached to a central Co atom:
(b) Diastereoisomers A and B have dipole moments of 6.5 D and 3.8 D, respectively. Which of your diastereoisomers is A and which is B?