For each of the following complexes, draw a crystal field energy-level diagram, assign the electrons to orbitals, and predict the number of unpaired electrons.
(b) [MnCl4]2- (tetrahedral)

 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry
Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry Problem 21.131b
Problem 21.131b Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
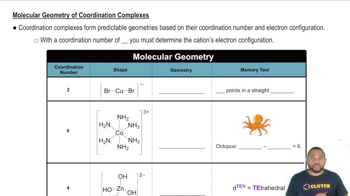
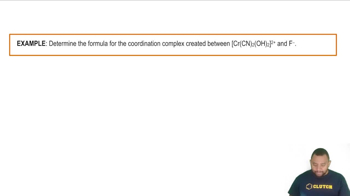
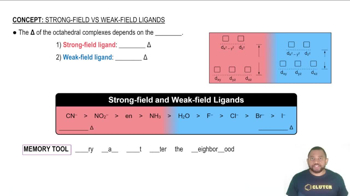
For each of the following complexes, draw a crystal field energy-level diagram, assign the electrons to orbitals, and predict the number of unpaired electrons.
(b) [MnCl4]2- (tetrahedral)
For each of the following complexes, describe the bonding using valence bond theory. Include orbital diagrams for the free metal ion and the metal ion in the complex. Indicate which hybrid orbitals the metal ion uses for bonding, and specify the number of unpaired electrons.
(b) [Ag(NH3)2]+
What is the systematic name for each of the following ions?
(c) [Co(CO3)3]3-
(d) [Pt(en)2(SCN)2]2+
Spinach contains a lot of iron but is not a good source of dietary iron because nearly all the iron is tied up in the oxalate complex [Fe(C2O4)3]3-.
(c) Draw a crystal field energy-level diagram for [Fe(C2O4)3]3-, and predict the number of unpaired electrons. (C2O42- is a weak-field bidentate ligand.)
The percent iron in iron ore can be determined by dissolving the ore in acid, then reducing the iron to Fe2+, and finally titrating the Fe2+ with aqueous KMnO4. The reaction products are Fe2+ and Mn2+.
(c) Draw a crystal field energy-level diagram for the reactants and products, MnO4-, 3Fe1H2O2642+, 3Fe1H2O2643+, and 3Mn1H2O2642+, and predict the number of unpaired electrons for each.
For each of the following complexes, draw a crystal field energy-level diagram, assign the electrons to orbitals, and predict the number of unpaired electrons.
(c) [Co(NCS)4]2- (tetrahedral)