The solubility product constants of PbSO4 and SrSO4 are 6.3 * 10-7 and 3.2 * 10-7, respectively. What are the values of 3SO4 2 - 4, 3Pb2 + 4, and 3Sr2 + 4 in a solution at equilibrium with both substances?
Ch.17 - Additional Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 17, Problem 108
The solubility product for Zn1OH22 is 3.0 * 10-16. The formation constant for the hydroxo complex, Zn1OH242 - , is 4.6 * 1017. What concentration of OH- is required to dissolve 0.015 mol of Zn1OH22 in a liter of solution?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the dissolution reaction for Zn(OH)_2: Zn(OH)_2 (s) \rightleftharpoons Zn^{2+} (aq) + 2OH^- (aq).
Write the expression for the solubility product (K_{sp}): K_{sp} = [Zn^{2+}][OH^-]^2.
Identify the formation reaction for the hydroxo complex: Zn^{2+} (aq) + 4OH^- (aq) \rightleftharpoons [Zn(OH)_4]^{2-} (aq).
Write the expression for the formation constant (K_f): K_f = \frac{[Zn(OH)_4^{2-}]}{[Zn^{2+}][OH^-]^4}.
Set up the equilibrium expressions and solve for [OH^-] using the given K_{sp} and K_f values, considering the total concentration of Zn(OH)_2 initially present.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
4mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Solubility Product (Ksp)
The solubility product constant (Ksp) is an equilibrium constant that applies to the solubility of sparingly soluble ionic compounds. It is defined as the product of the molar concentrations of the ions, each raised to the power of their coefficients in the balanced equation. For Zn(OH)2, Ksp = [Zn^2+][OH^-]^2, which helps determine the concentration of ions in a saturated solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Solubility Product Constant
Formation Constant (Kf)
The formation constant (Kf) quantifies the stability of a complex ion in solution. It is defined as the equilibrium constant for the formation of a complex from its constituent ions. In this case, Kf for Zn(OH)4^2- indicates how readily Zn^2+ ions react with OH- ions to form the hydroxo complex, influencing the solubility of Zn(OH)2 in the presence of hydroxide ions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
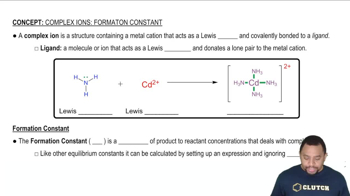
Complex Ions and Formation Constant
Equilibrium and Le Chatelier's Principle
Equilibrium in chemistry refers to the state where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal, resulting in constant concentrations of reactants and products. Le Chatelier's Principle states that if a system at equilibrium is disturbed, it will shift in a direction that counteracts the disturbance. This principle is crucial for understanding how changes in OH- concentration affect the solubility of Zn(OH)2 and the formation of its hydroxo complex.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Le Chatelier's Principle
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
The value of Ksp for Cd(OH)2 is 2.5 × 10-14. (a) What is the molar solubility of Cd(OH)2?
Textbook Question
The value of Ksp for Cd(OH)2 is 2.5 × 10–14. (b) The solubility of Cd(OH)2 can be increased through formation of the complex ion CdBr42- (Kf = 5 × 103). If solid Cd(OH)2 is added to a NaBr solution, what is the initial concentration of NaBr needed to increase the molar solubility of Cd(OH)2 to 1.0 × 10-3 mol/L?
Textbook Question
(a) Write the net ionic equation for the reaction that occurs when a solution of hydrochloric acid (HCl) is mixed with a solution of sodium formate 1NaCHO22.
