Textbook Question
Write balanced chemical equations for each of the following reactions: (d) Nitrogen dioxide dissolves in water to form nitric acid and nitric oxide.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Write balanced chemical equations for each of the following reactions: (d) Nitrogen dioxide dissolves in water to form nitric acid and nitric oxide.
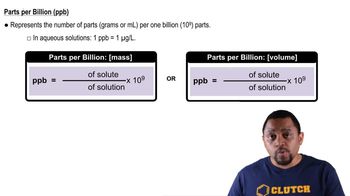
(b) Will Mg(OH)2 precipitate when 4.0 g of Na2CO3 is added to 1.00 L of a solution containing 125 ppm of Mg2+?
(b) Concentrations of lead in the bloodstream are often quoted in units of μg/dL. Averaged over the entire country, the mean concentration of lead in the blood was measured to be 1.6 μg/dL in 2008. Express this concentration in ppb.
The estimated average concentration of NO2 in air in the United States in 2006 was 0.016 ppm. (a) Calculate the partial pressure of the NO2 in a sample of this air when the atmospheric pressure is 755 torr (99.1 kPa).