Balance the following equations: d. AlCl3(𝑠)+Ca3N2(𝑠)⟶AlN(𝑠)+CaCl2(𝑠)
Ch.3 - Chemical Reactions and Reaction Stoichiometry

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 3, Problem 14c
Balance the following equations: c. NaHCO3(𝑠)+H2SO4(𝑎𝑞)⟶CO2(𝑔)+H2O(𝑙)+Na2SO4(𝑎𝑞)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the reactants and products in the equation. Reactants are NaHCO3 (sodium bicarbonate) and H2SO4 (sulfuric acid). Products are CO2 (carbon dioxide), H2O (water), and Na2SO4 (sodium sulfate).
Write the unbalanced chemical equation: NaHCO3(s) + H2SO4(aq) → CO2(g) + H2O(l) + Na2SO4(aq).
Balance the sodium (Na) atoms first. Since there are two sodium atoms in Na2SO4 on the product side, you need two NaHCO3 molecules on the reactant side.
Next, balance the hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms. Check the number of hydrogen and oxygen atoms on both sides of the equation to ensure they are equal.
Finally, verify that all other elements are balanced and adjust coefficients if necessary to ensure the total number of atoms for each element is the same on both sides of the equation.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Balancing Chemical Equations
Balancing chemical equations involves ensuring that the number of atoms for each element is the same on both sides of the equation. This is based on the law of conservation of mass, which states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Coefficients are used to adjust the quantities of reactants and products to achieve balance.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Balancing Chemical Equations
Types of Chemical Reactions
The reaction between sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is an example of an acid-base reaction, where an acid reacts with a bicarbonate to produce carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and a salt (Na2SO4). Understanding the type of reaction helps predict the products formed and the stoichiometry involved in balancing the equation.
Recommended video:
Guided course
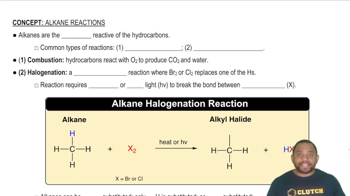
Common Types of Alkane Reactions
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is the calculation of reactants and products in chemical reactions based on their molar ratios. It allows chemists to determine how much of each substance is needed or produced in a reaction. In balancing equations, stoichiometric coefficients are essential for ensuring that the proportions of reactants and products are correct according to the balanced equation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Stoichiometry Concept
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Balance the following equations: b. C5H10O2(𝑙)+O2(𝑔)⟶CO2(𝑔)+H2O(𝑔)
Textbook Question
Balance the following equations: b. WCl6(𝑠)+Na2S(𝑠)⟶WS2(𝑠)+NaCl(𝑠)+S(𝑠)
Textbook Question
Balance the following equations: d, NaN3(𝑠)+HNO2(𝑎𝑞)⟶N2(𝑔)+NO(𝑔)+NaOH(𝑎𝑞)
Textbook Question
Write balanced chemical equations corresponding to each of the following descriptions: c. Solid zinc metal reacts with sulfuric acid to form hydrogen gas and an aqueous solution of zinc sulfate.
Textbook Question
Write balanced chemical equations to correspond to each of the following descriptions: (a) When sulfur trioxide gas reacts with water, a solution of sulfuric acid forms. (b) Boron sulfide, B2S3(s), reacts violently with water to form dissolved boric acid, H3BO3, and hydrogen sulfide gas.
