Textbook Question
From a plot of the concentration–time data in Worked Example 14.9, estimate: (b) the initial rate of decomposition of NO2.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

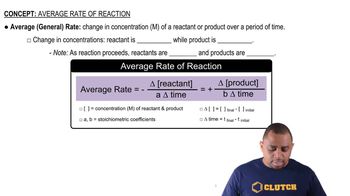
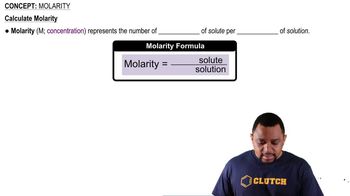
From a plot of the concentration–time data in Worked Example 14.9, estimate: (b) the initial rate of decomposition of NO2.
Ammonia is manufactured in large amounts by the reaction
N2(g) + 3 H2(g) → 2 NH3(g)
(a) How is the rate of consumption of H2 related to the rate of consumption of N2?