Based on sales data over the past year, the owner of a DVD store devises the demand function D(p) = 40 - 2p, where D(p) is the number of DVDs that can be sold in one day at a price of p dollars.
Find the elasticity function for this demand function.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: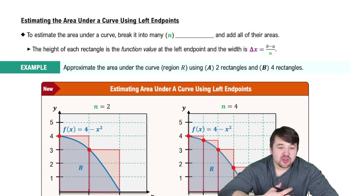

 4:16m
4:16mMaster Intro To Related Rates with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning