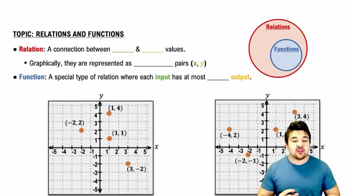
Let . <IMAGE>
Calculate for each value of in the following table.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 6:47m
6:47mMaster Finding Limits Numerically and Graphically with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning