Which of the following cell structures would you expect to be most important in the growth of bacteria on the surface of your teeth?
a. Cell wall
b. Fimbriae
c. Flagella
d. Cilia

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

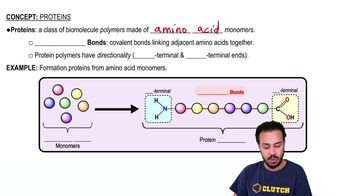
Which of the following cell structures would you expect to be most important in the growth of bacteria on the surface of your teeth?
a. Cell wall
b. Fimbriae
c. Flagella
d. Cilia
Cells that line your intestines are known to possess a large number of membrane proteins that transport small molecules and ions across the plasma membrane. Which of the following cell structures would you expect to be required for this characteristic of the cells?
a. The endoplasmic reticulum
b. Peroxisomes
c. Lysosomes
d. The cell wall
Most of the proteins that enter the nucleus possess a nuclear localization signal (NLS), even if they are small enough to pass through the nuclear pore complex unhindered. Why would a small protein have an NLS, when it naturally diffuses across the nuclear pore complex without one?
When analyzing a sample of cells from a patient, you find the lysosomes are filled with undigested material. This observation makes you think that the lysosomes are not functioning properly. What are three different defects that could be responsible for malfunctioning lysosomes?
George Palade's research group used the pulse–chase assay to elucidate the secretory pathway in pancreatic cells. If they had instead performed this assay on muscle cells, where would you expect the labeled proteins to end up during the chase?
(Muscle cells consist primarily of actin and myosin filaments and have high energy demands for muscle contraction.)