Evolutionary biologist Hopi Hoekstra and colleagues have hypothesized that the burrow-digging behavior of mice (and the resulting shape of their underground burrows) is heritable—innate and not learned. Design an experiment to test this hypothesis.

<Image>
Mass strandings of whales occur on beaches near military exercises where sonar is used, raising concerns about the effects of human-generated underwater sounds on animal behavior. Scientists are collecting behavioral data on several species of whales to find out how sonar affects them.
Using the graph, estimate the number of minutes of foraging per hour before and after the sound exposure. Then predict the effect of sonar on the fitness of blue whales. Explain your reasoning.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Foraging Behavior

Impact of Sound Exposure
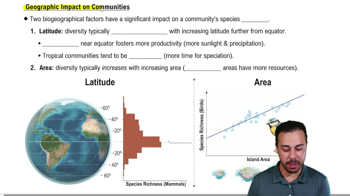
Fitness and Survival

<Image>
Mass strandings of whales occur on beaches near military exercises where sonar is used, raising concerns about the effects of human-generated underwater sounds on animal behavior. Scientists are collecting behavioral data on several species of whales to find out how sonar affects them.
Whales communicate with one another using sound. What is one benefit and one cost to whales of using sound to communicate underwater?
<Image>
Mass strandings of whales occur on beaches near military exercises where sonar is used, raising concerns about the effects of human-generated underwater sounds on animal behavior. Scientists are collecting behavioral data on several species of whales to find out how sonar affects them.
Researchers followed tagged blue whales to observe how they respond to simulated military sonar—using sound levels much lower than those typically used during military exercises. Analyze the sample of data below for one individual blue whale and summarize the behavioral effect of the sound exposure.
<Image>
Mass strandings of whales occur on beaches near military exercises where sonar is used, raising concerns about the effects of human-generated underwater sounds on animal behavior. Scientists are collecting behavioral data on several species of whales to find out how sonar affects them.
Predict why the whale foraged at a depth of 100–170 m.
a. The whale learned to forage at this depth from its mother.
b. The whale had an innate instinct to feed at this depth.
c. The whale's food was most plentiful at this depth.
d. The whale could not dive any deeper than this depth.
<Image>
Mass strandings of whales occur on beaches near military exercises where sonar is used, raising concerns about the effects of human-generated underwater sounds on animal behavior. Scientists are collecting behavioral data on several species of whales to find out how sonar affects them.
The researchers also measured the speed and direction of whale swimming in response to the sound exposure. Whales increase their speed and swim away from the direction of sound. Design a study to test the hypothesis that this behavior leads to beach strandings. Note that you will not receive permission to conduct the study if your actions are likely to cause strandings to occur.
<Image>
Mass strandings of whales occur on beaches near military exercises where sonar is used, raising concerns about the effects of human-generated underwater sounds on animal behavior. Scientists are collecting behavioral data on several species of whales to find out how sonar affects them.
There are debates about what action the military should take to avoid harming the whales. How could you apply cost–benefit analysis to address this problem?
