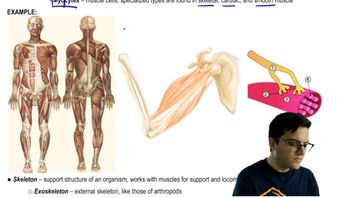
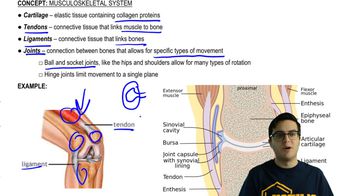
Which of the following statements regarding control of muscle tissue is/are correct? Select True or False for each statement.
T/F All skeletal muscles are voluntary.
T/F Cardiac muscle is involuntary.
T/F Some smooth muscle tissues are voluntary, and others are involuntary.
T/F Parasympathetic and sympathetic neurons innervate skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle tissues.