Textbook Question
Which protostome phyla successfully made the transition from water to land? Select True or False for each phylum.
T/FMollusca
T/FArthropoda
T/FAnnelida
T/FNematoda

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance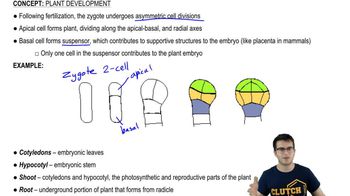
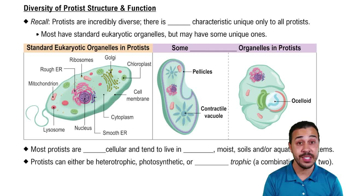
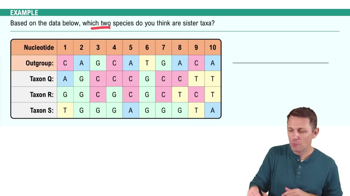
Which protostome phyla successfully made the transition from water to land? Select True or False for each phylum.
T/FMollusca
T/FArthropoda
T/FAnnelida
T/FNematoda
Propose an explanation for why annelids and arthropods were thought to be closely related, before phylogenetic analyses in the late 1990s.