Textbook Question
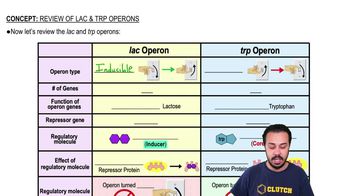
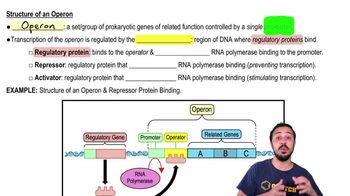
In the lac operon, the repressor inhibits transcription when
a. The repressor is bound to the inducer.
b. The repressor is not bound to the inducer.
c. The repressor is bound to glucose.
d. The repressor is not bound to the operator.
1
views