Textbook Question
Which clade does not include humans?
a. Synapsids
b. Lobe-fins
c. Diapsids
d. Osteichthyans

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
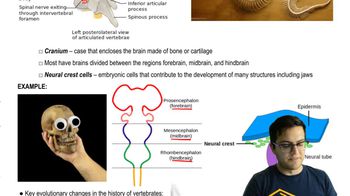

Which clade does not include humans?
a. Synapsids
b. Lobe-fins
c. Diapsids
d. Osteichthyans
As hominins diverged from other primates, which of the following appeared first?
a. Reduced jawbones
b. An enlarged brain
c. The making of stone tools
d. Bipedal locomotion
Which of the following could be considered the most recent common ancestor of living tetrapods?
a. A sturdy-finned, shallow-water lobe-fin whose appendages had skeletal supports similar to those of terrestrial vertebrates
b. An armored, jawed placoderm with two pairs of appendages
c. An early ray-finned fish that developed bony skeletal supports in its paired fins
d. A salamander that had legs supported by a bony skeleton but moved with the side-to-side bending typical of fishes