Choose the pair of terms that correctly completes this sentence: Catabolism is to anabolism as ____________ is to ____________.
a. exergonic; spontaneous
b. exergonic; endergonic
c. free energy; entropy
d. work; energy

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
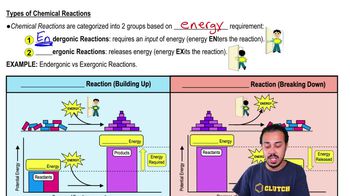
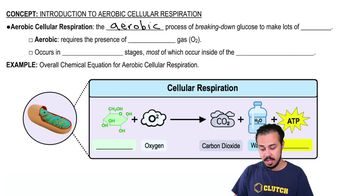
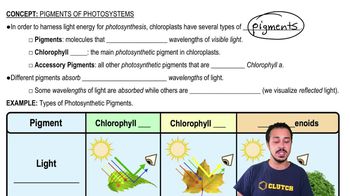
Choose the pair of terms that correctly completes this sentence: Catabolism is to anabolism as ____________ is to ____________.
a. exergonic; spontaneous
b. exergonic; endergonic
c. free energy; entropy
d. work; energy
Most cells cannot harness heat to perform work because
a. Heat does not involve a transfer of energy.
b. Cells do not have much thermal energy; they are relatively cool.
c. Temperature is usually uniform throughout a cell.
d. Heat can never be used to do work.
If an enzyme in solution is saturated with substrate, the most effective way to obtain a faster yield of products is to
a. Add more of the enzyme.
b. Heat the solution to 90°C.
c. Add more substrate.
d. Add a noncompetitive inhibitor.
Some bacteria are metabolically active in hot springs because
a. They are able to maintain a lower internal temperature.
b. High temperatures make catalysis unnecessary.
c. Their enzymes have high optimal temperatures.
d. Their enzymes are completely insensitive to temperature.
If an enzyme is added to a solution where its substrate and product are in equilibrium, what will occur?
a. Additional substrate will be formed.
b. The reaction will change from endergonic to exergonic.
c. The free energy of the system will change.
d. Nothing; the reaction will stay at equilibrium.