Which structure is part of the endomembrane system?
a. Mitochondrion
b. Golgi apparatus
c. Chloroplast
d. Centrosome

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
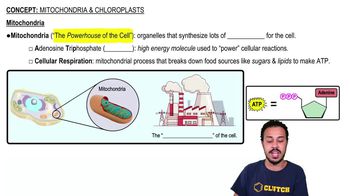
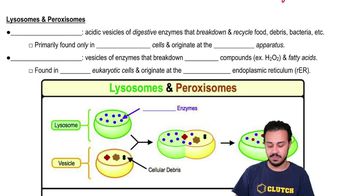
Which structure is part of the endomembrane system?
a. Mitochondrion
b. Golgi apparatus
c. Chloroplast
d. Centrosome
Which structure is common to plant and animal cells?
a. Chloroplast
b. Central vacuole
c. Mitochondrion
d. Centriole
Which of the following is present in a prokaryotic cell?
a. Mitochondrion
b. Ribosome
c. Nuclear envelope
d. Chloroplast
Which cell would be best for studying lysosomes?
a. Muscle cell
b. Nerve cell
c. Bacterial cell
d. Phagocytic white blood cell
From memory, draw two eukaryotic cells. Label the structures listed here and show any physical connections between the internal structures of each cell: nucleus, rough ER, smooth ER, mitochondrion, centrosome, chloroplast, vacuole, lysosome, microtubule, cell wall, ECM, microfilament, Golgi apparatus, intermediate filament, plasma membrane, peroxisome, ribosome, nucleolus, nuclear pore, vesicle, flagellum, microvilli, plasmodesma.