Textbook Question
Blood returning to the mammalian heart in a pulmonary vein drains first into the
a. Left atrium
b. Right atrium
c. Left ventricle
d. Right ventricle

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
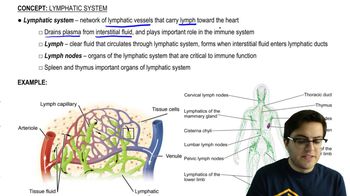

Blood returning to the mammalian heart in a pulmonary vein drains first into the
a. Left atrium
b. Right atrium
c. Left ventricle
d. Right ventricle
Pulse is a direct measure of
a. Blood pressure.
b. Stroke volume.
c. Cardiac output.
d. Heart rate.
When you hold your breath, which of the following blood gas changes first leads to the urge to breathe?
a. Rising O2
b. Falling O2
c. Rising CO2
d. Falling CO2