Textbook Question
The distinction between sponges and other animal phyla is based mainly on the absence versus the presence of
a. A body cavity
b. A complete digestive tract
c. Mesoderm
d. Tissues

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
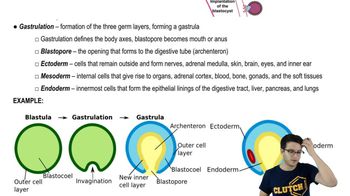
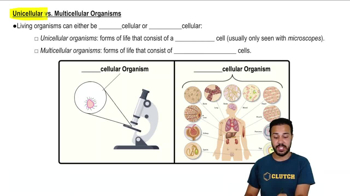

The distinction between sponges and other animal phyla is based mainly on the absence versus the presence of
a. A body cavity
b. A complete digestive tract
c. Mesoderm
d. Tissues
Which of the following was probably an important factor in bringing about the Cambrian explosion?
a. The movement of animals onto land
b. An increase in the concentration of atmospheric nitrogen
c. The emergence of predator-prey relationships
d. The origin of bilaterian animals
Based on the tree in Figure 32.11, which statement is true?
A. The animal kingdom is not monophyletic.
B. The Acoela are more closely related to echinoderms than to annelids.
C. Sponges are basal animals.
D. Bilaterians do not form a clade.