A cell that begins mitosis with 46 chromosomes produces daughter cells with ________ chromosomes.
a. 13
b. 23
c. 46
d. 92

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
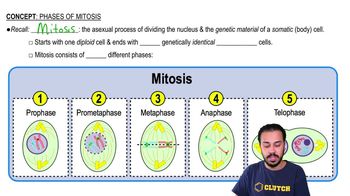
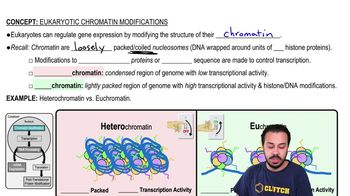
A cell that begins mitosis with 46 chromosomes produces daughter cells with ________ chromosomes.
a. 13
b. 23
c. 46
d. 92
The centromere is a region at which ________.
a. Sister chromatids are attached to each other.
b. Metaphase chromosomes align.
c. The tips of chromosomes are found.
d. The nucleus is located.
Mitosis ________.
a. Occurs only in cancerous cells.
b. Occurs only in skin cells.
c. Produces daughter cells that are exact genetic copies of the parent cell.
d. Results in the production of three different cells.
Sister chromatids ________.
a. Are two different chromosomes attached to each other.
b. Are exact copies of one chromosome that are attached to each other.
c. Arise from the centrioles.
d. Are broken down by mitosis.
e. Are chromosomes that carry different genes.
DNA polymerase ________.
a. Attaches sister chromatids at the centromere.
b. Synthesizes daughter DNA molecules from fats and phospholipids.
c. Is the enzyme that facilitates DNA synthesis.
d. Causes cancer cells to stop dividing.
If a cell at G1 contains four picograms of DNA, how many picograms of DNA will it contain at the end of the S phase of the cell cycle?
a. 0
b. 2
c. 4
d. 8