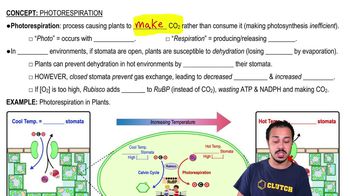
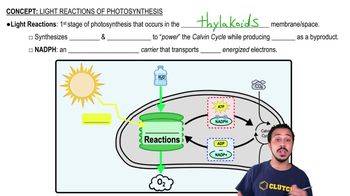
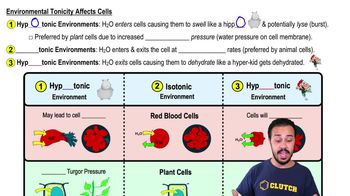
Which of the following does not occur during the light reactions of photosynthesis?
a. Water is released.
b. Electrons from chlorophyll are moved to a higher-energy state by light.
c. ATP is produced.
d. NADPH is produced to carry electrons to the light-independent reactions.
e. Oxygen is produced when water is split.