
The theory of common descent states that all modern organisms
a. Can change in response to environmental change
b. Descended from a single common ancestor
c. Descended from one of many ancestors that originally arose on Earth
d. Have not evolved
e. Can be arranged in a hierarchy from 'least evolved' to 'most evolved'
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Theory of Common Descent
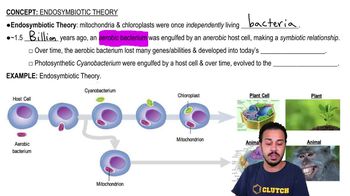
Evolution

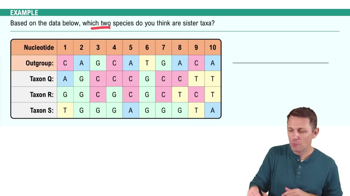
Phylogenetic Tree
In science, a theory is a(n)
a. Educated guess
b. Inference based on a lack of scientific evidence
c. Idea with little experimental support
d. Body of scientifically acceptable general principles
e. Statement of fact
Add labels to the figure that follows, which illustrates how Mycobacterium tuberculosis evolves when it is exposed to an antibiotic.
The DNA sequence for the same gene found in several species of mammals_________.
a. Is identical among all species.
b. Is equally different between all pairs of mammal species.
c. Is more similar between closely related species than between distantly related species.
d. Provides evidence for the hypothesis of common descent
e. More than one of the above is correct.
Marsupial mammals give birth to young that complete their development in a pouch on the mother's abdomen. All the native mammals of Australia are marsupials, while these types of mammals are absent or uncommon on other continents. This observation is an example of
a. Developmental evidence for evolution
b. Biogeographic evidence for evolution
c. Genetic evidence for evolution
d. Fossil evidence for evolution
e. Not useful evidence for evolution
Even though marsupial mammals give birth to live young, an eggshell forms briefly early in their development. This is evidence that:
a. Marsupials share a common ancestor with some egg-laying species
b. Marsupials are not really mammals
c. All animals arose from a common ancestor.
d. Marsupial mammals were separately created by God
e. The fossil record of marsupial mammals is incorrect
