Back
BackProblem 1
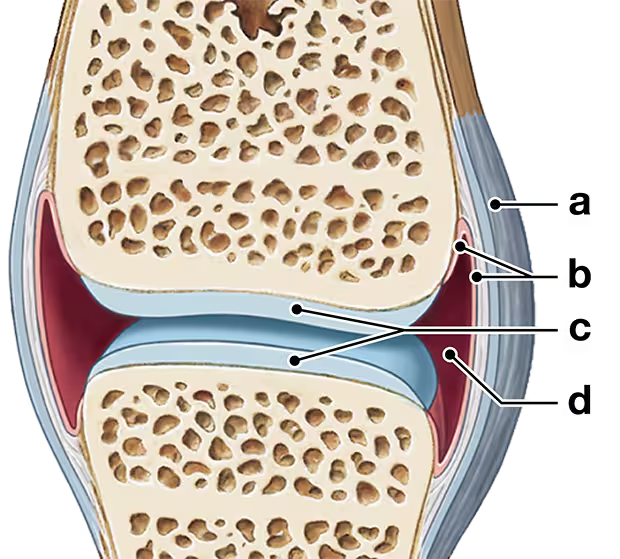
Label the structures in the following illustration of a synovial joint.
Problem 2
A synarthrosis located between the bones of the skull is a
(a) Symphysis
(b) Syndesmosis
(c) Synchondrosis
(d) Suture
Problem 3
The joint between adjacent vertebral bodies is a
(a) Syndesmosis
(b) Symphysis
(c) Synchondrosis
(d) Synostosis.
Problem 4
The anterior joint between the two pubic bones is a
(a) Synchondrosis
(b) Synostosis
(c) Symphysis
(d) Synarthrosis
Problem 5
Joints typically located between the ends of adjacent long bones are
(a) Synarthroses
(b) Amphiarthroses
(c) Diarthroses
(d) Symphyses
Problem 6
The function of the articular cartilage is:
(a) To reduce friction
(b) To prevent bony surfaces from contacting one another
(c) To provide lubrication
(d) Both a and b
Problem 7
Which of the following is not a function of synovial fluid?
(a) Shock absorption
(b) Nutrient distribution
(c) Maintenance of ionic balance
(d) Lubrication of the articular surfaces
(e) Waste disposal
Problem 18
Subacromial, subcoracoid, and subscapular bursae reduce friction in the____joint.
(a) hip
(b) knee
(c) elbow
(d) shoulder
Problem 19
Although the knee joint is only one joint, it resembles____ separate joints.
(a) two
(b) three
(c) four
(d) five
(e) six
Problem 21
The hip is an extremely stable joint because it has
(a) A complete bony socket
(b) A strong joint capsule
(c) Supporting ligaments
(d) All of these
Problem 22
How does a meniscus (articular disc) function in a joint?
Problem 23
Partial or complete dislocation of the acromioclavicular joint is called a(n)___ .
Problem 27
List the six different types of diarthroses, and give an example of each.