Back
BackProblem 1
More than one choice may apply. The major endocrine organs of the body
a. Tend to be very large organs
b. Are closely connected with each other
c. All contribute to the same function (digestion)
d. Tend to lie near the midline of the body
Problem 2
More than one choice may apply. Which is generally true of hormones?
a. Exocrine glands produce them.
b. They travel throughout the body in the blood.
c. They affect only non–hormone-producing organs.
d. All steroid hormones produce very similar physiological effects in the body.
Problem 3
More than one choice may apply. Which of the following hormones is (are) secreted by neurons?
a. Oxytocin
b. Insulin
c. ADH
d. Cortisol
Problem 4
More than one choice may apply.
ANP, the hormone secreted by the heart, has exactly the opposite function to this hormone secreted by the outermost zone of the adrenal cortex.
a. Epinephrine
b. Cortisol
c. Aldosterone
d. Testosterone
Problem 4e
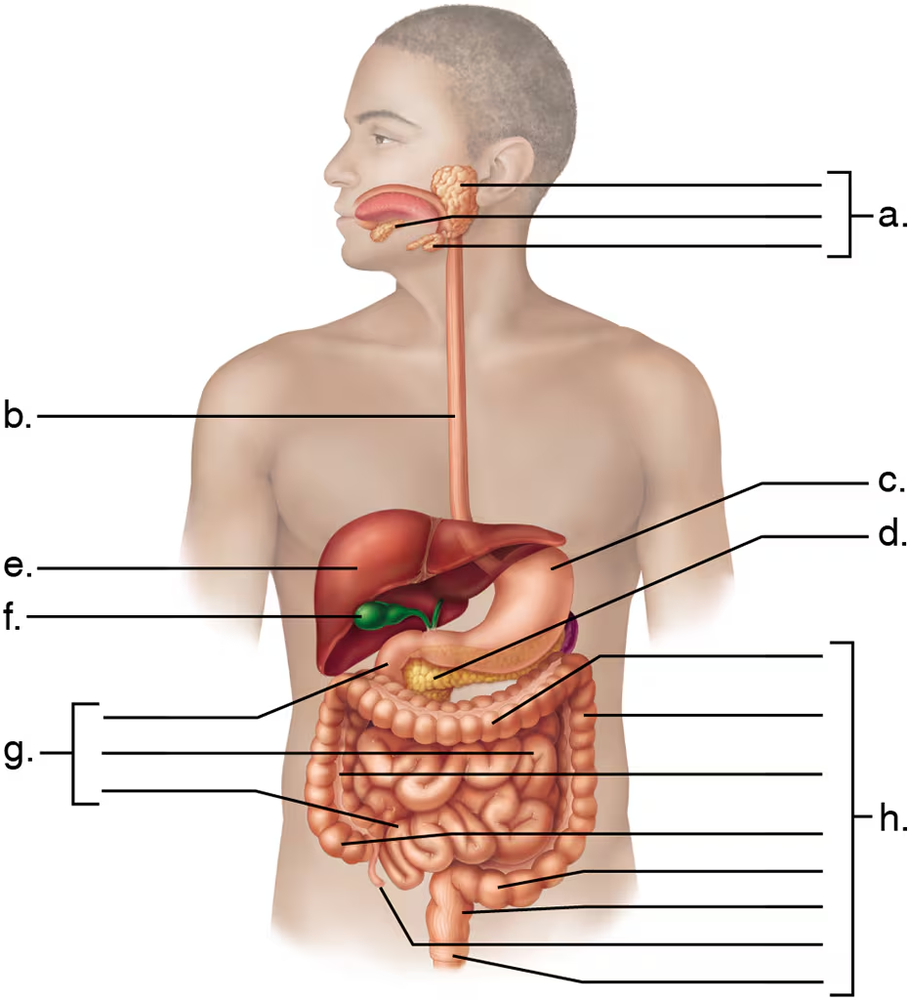
Match the letter of the digestive organ shown in the figure with its function.
___ produces both endocrine and exocrine secretions
Problem 5
More than one choice may apply.
Hormones that act directly or indirectly to elevate the blood glucose level include which of the following?
a. GH
b. Cortisol
c. Insulin
d. ACTH
Problem 6
More than one choice may apply.
Hypertension may result from hypersecretion of
a. Thyroxine
b. Cortisol
c. Aldosterone
d. ADH
Problem 7
More than one choice may apply.
Hormones that regulate mineral (salt) levels include
a. Calcitonin
b. Aldosterone
c. Atrial natriuretic peptide
d. Glucagon
Problem 8
More than one choice may apply.
Which of the following is given as a drug to reduce inflammation?
a. Epinephrine
b. Cortisol
c. Aldosterone
d. ADH
Problem 9
More than one choice may apply. The element needed for thyroid gland function is
a. Potassium
b. Iodine
c. Calcium
d. Manganese
Problem 10
More than one choice may apply.
Hormones that act to decrease the blood glucose level include
a. Insulin
b. Glucagon
c. Epinephrine
d. Growth hormone
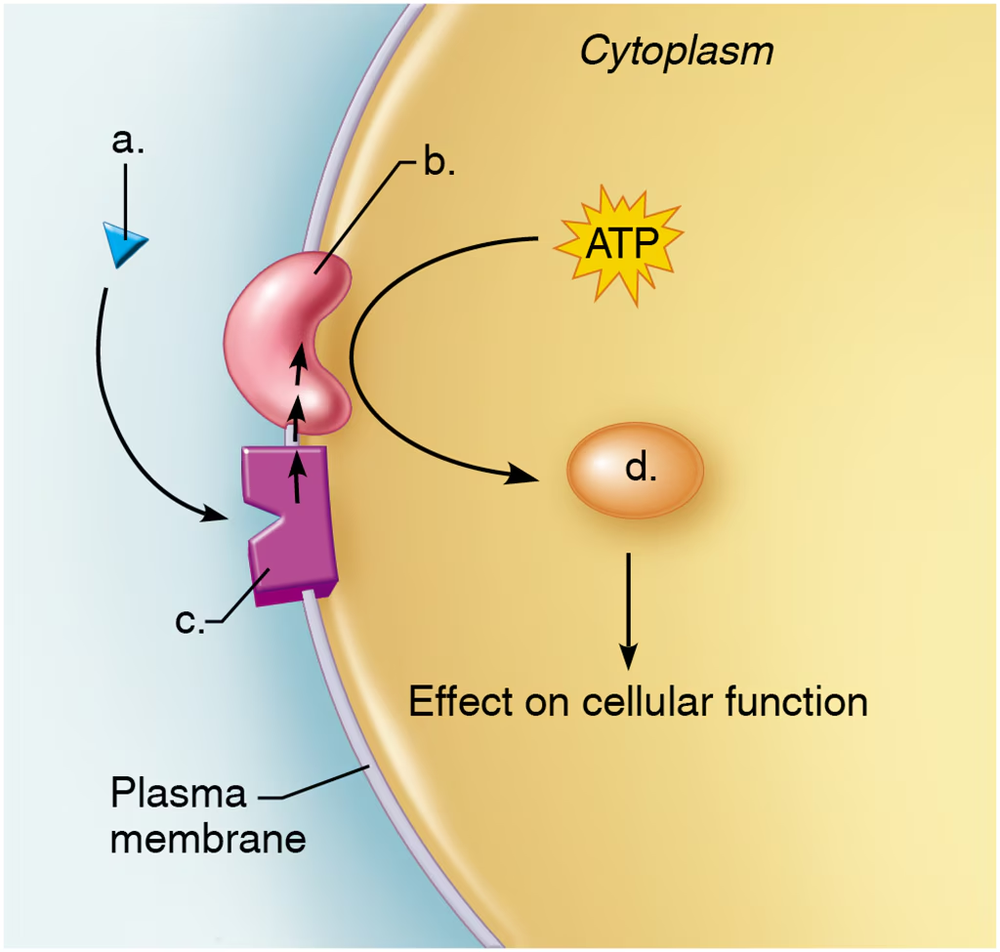
Problem 10
More than one choice may apply. In the hormone-signaling pathway represented in the figure,_________ is the first messenger, and _______is the second messenger that will signal a change in cell activity.
Problem 11
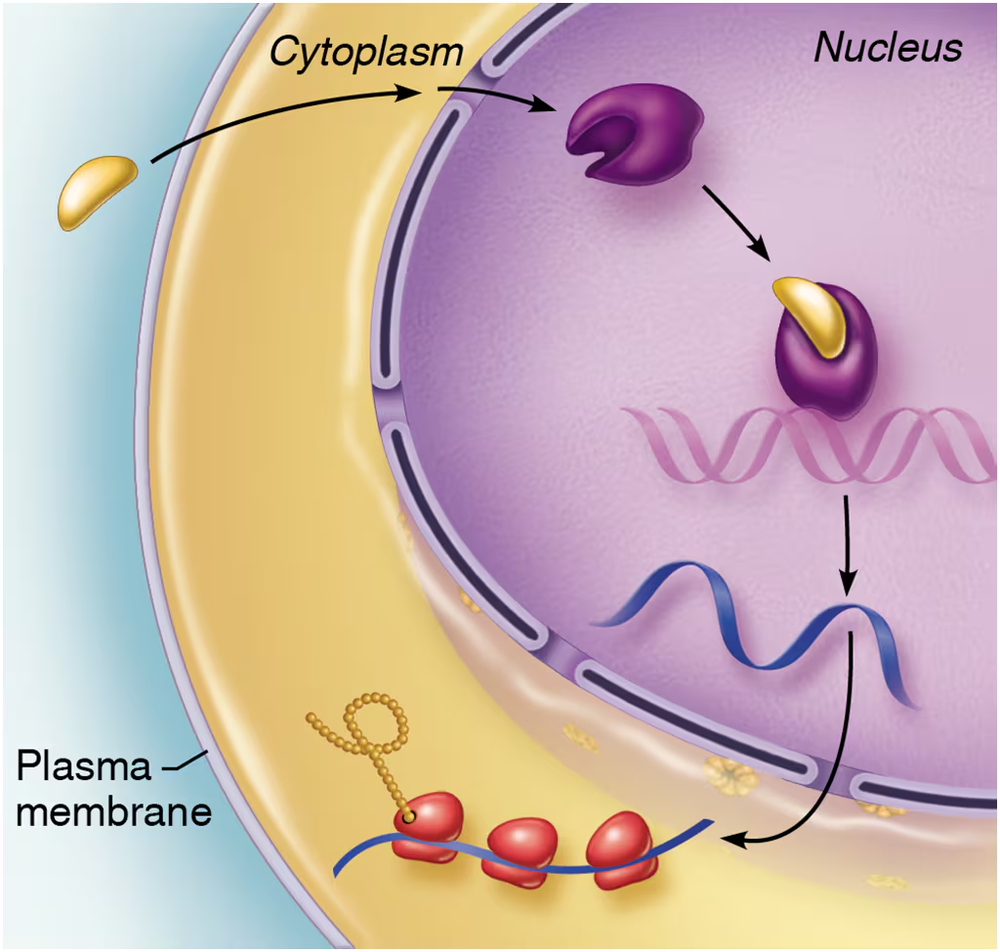
Explain what mechanism of hormone action is occurring in this image. How does it work? Give an example of a hormone that uses this mechanism.
Problem 11
More than one choice may apply.
Which events occur shortly after eating?
a. Use of amino acids as a major source of energy
b. Lipogenesis (and fat deposit)
c. Breakdown of fat reserves
d. Increased uptake of glucose by skeletal muscles and other body tissues
Problem 12
Describe the chemical nature of hormones.
Problem 13
Provide one example for each way endocrine glands are stimulated to release their hormones.
Problem 14
Describe the body location of each of the following endocrine organs: anterior pituitary, pineal gland, thymus, pancreas, ovaries, testes. Then, for each organ, name its hormones and their effect(s) on body processes. Finally, for each hormone, list the important results of its hypersecretion or hyposecretion.
Problem 15
Name two endocrine-producing glands (or regions) that are important in the stress response, and explain why they are important.
Problem 16
The anterior pituitary is often referred to as the master endocrine gland, but it too has a 'master.' What controls the release of hormones by the anterior pituitary?
Problem 17
Name three hormone antagonists of insulin and one of PTH.
Problem 18
Two hormones are closely involved in the regulation of the fluid and electrolyte balance of the body. Name them, and explain their effects on their common target organ.
Problem 19
The parents of 14-year-old Megan are concerned about her height because she is only 4 feet tall and they are both close to 6 feet tall. After tests by their doctor, certain hormones are prescribed for the girl. What is the probable diagnosis? What hormones are prescribed, and why might the girl expect to reach normal height?
Problem 20
Mr. Flores brings his wife to the clinic, concerned about her nervousness, heart palpitations, and excessive sweating. Tests show hyperglycemia and hypertension. What hormones are probably being hypersecreted? What is the cause? What physical factors allow you to rule out thyroid problems?
Problem 21
Melissa, age 40, comes to the clinic, troubled by swelling in her face and unusual fat deposition on her back and abdomen. She reports that she bruises easily. Blood tests show an elevated glucose level. What is your diagnosis, and which glands might be causing the problem?