Back
BackProblem 8
Which of the following is not a skin structure?
a. Nerve fiber
b. Hair papilla
c. Hair
d. Nail
Problem 9d
Match the appropriate structure with the proper description and/or function.
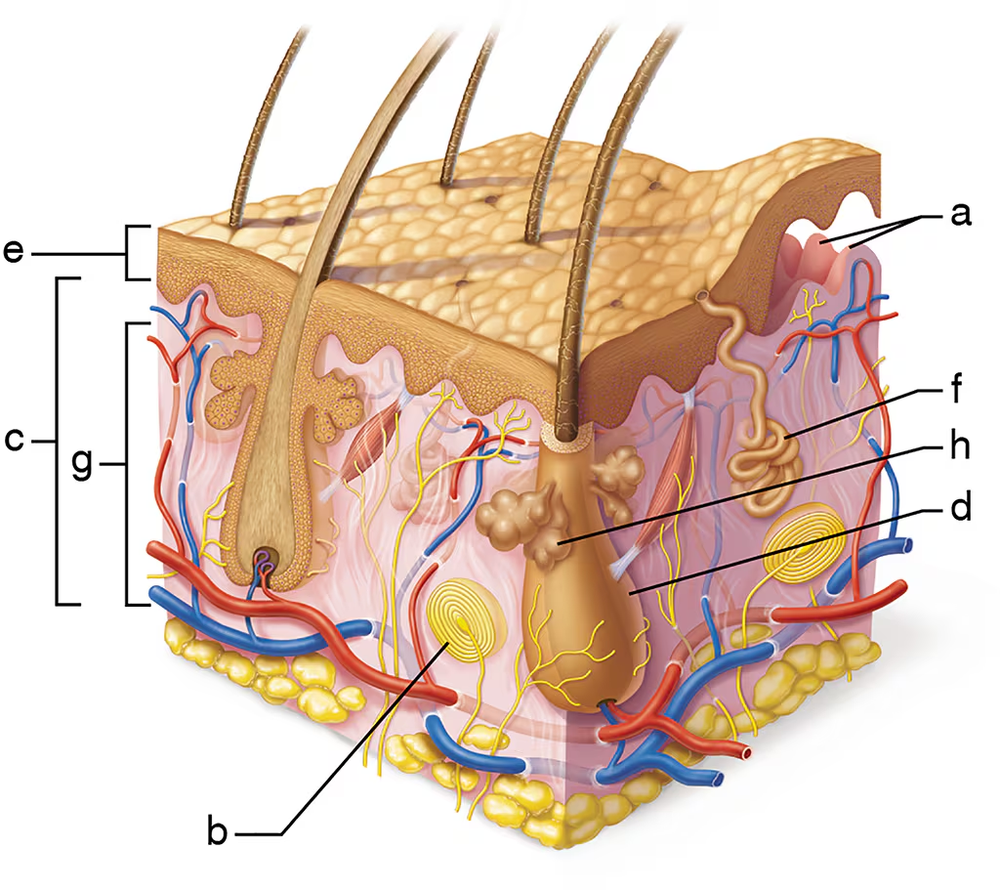
4. Cause Fingerprints
a. Dermal papillae
b. Lamellar corpuscles
c. Dermis
d. Hair follicle
e. Epidermis
f. Eccrine sweat gland
g. Reticular layer
h. Sebaceous glands
Problem 9f
Match the appropriate structure with the proper description and/or function.
1. Made of dense, irregular connective tissue
2. Produce sebum
3. Helps regulate body temperature by producing sweat
4. Cause fingerprints
5. Houses the hair root
6. Superficial keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
7. Deep pressure receptors
8. Vascular layer that houses skin appendages
a. Dermal papillae
b. Lamellar corpuscles
c. Dermis
d. Hair follicle
e. Epidermis
f. Eccrine sweat gland
g. Reticular layer
h. Sebaceous glands
Problem 9g
Match the appropriate structure with the proper description and/or function.
1. Made of dense, irregular connective tissue
2. Produce sebum
3. Helps regulate body temperature by producing sweat
4. Cause fingerprints
5. Houses the hair root
6. Superficial keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
7. Deep pressure receptors
8. Vascular layer that houses skin appendages
a. Dermal papillae
b. Lamellar corpuscles
c. Dermis
d. Hair follicle
e. Epidermis
f. Eccrine sweat gland
g. Reticular layer
h. Sebaceous glands
Problem 9h
Match the appropriate structure with the proper description and/or function.
1. Made of dense, irregular connective tissue
2. Produce sebum
3. Helps regulate body temperature by producing sweat
4. Cause fingerprints
5. Houses the hair root
6. Superficial keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
7. Deep pressure receptors
8. Vascular layer that houses skin appendages
a. Dermal papillae
b. Lamellar corpuscles
c. Dermis
d. Hair follicle
e. Epidermis
f. Eccrine sweat gland
g. Reticular layer
h. Sebaceous glands
Problem 11
From what types of damage does the skin protect the body?
Problem 15
Name three changes that occur in the skin as one ages.
Problem 18
Both newborn infants and aged individuals have very little subcutaneous tissue. How does this affect their sensitivity to cold environmental temperature?
Problem 18
More than one choice may apply.
Which layer of the heart wall is an endothelium?
a. Endocardium
b. Myocardium
c. Epicardium
d. Pericardium
Problem 19
Roger, a 40-year-old man who loves spending time on the beach, is complaining to you that his suntan made him popular when he was young—but now his face is all wrinkled, and he has several darkly pigmented moles that are growing rapidly and are as big as large coins. He shows you the moles, and immediately you think “ABCDE.” What does that mean, and why should he be concerned?
Problem 20
Rebecca, the mother of a 13-month-old infant, brings her child to the clinic because his skin has turned orange. Why does the pediatrician inquire about the child’s diet?
Problem 21
Mr. Grayson is receiving a drug treatment transdermally (through the skin). Explain why drugs delivered by this route are fat-soluble rather than water-soluble.
Problem 22
A burn victim exhibits a red and swollen arm with blistering; a hand that has been charred black, exposing bone; and a cheek that appears blanched. How serious is each burn, and is this patient critical? Explain.