Back
BackProblem 3
More than one choice may apply.
During inspiration, intrapulmonary pressure is
a. Greater than atmospheric pressure
b. Less than atmospheric pressure
c. Greater than intrapleural pressure
d. Less than intrapleural pressure
Problem 6
More than one choice may apply.
Which of the following changes will accompany the loss of lung elasticity associated with aging?
a. Increase in tidal volume
b. Increase in inspiratory reserve volume
c. Increase in residual volume
d. Increase in vital capacity
Problem 8
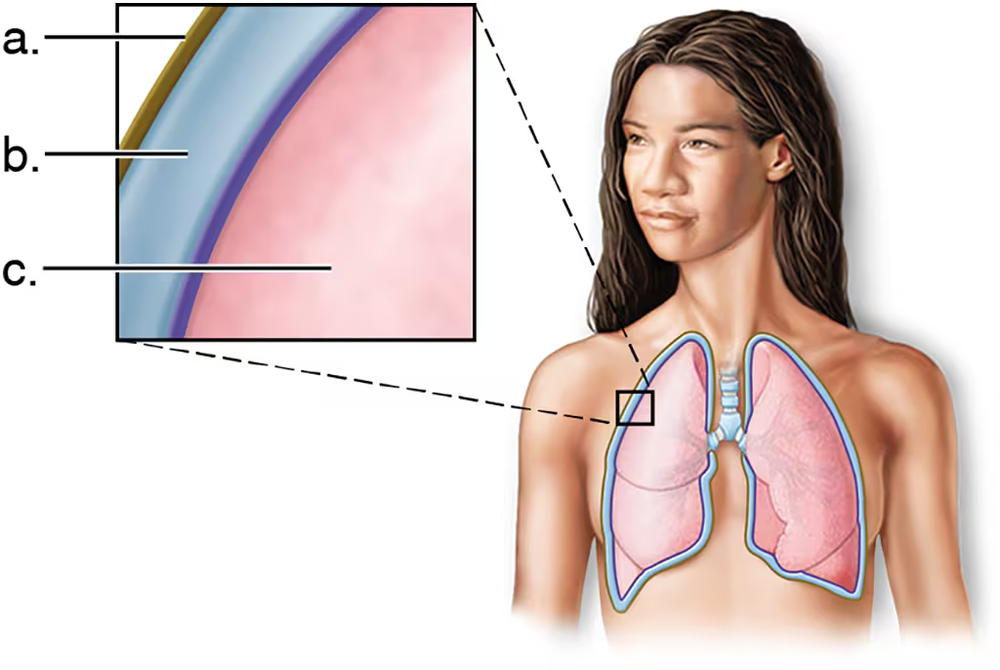
Which of the following represents intrapleural pressure?
Problem 9
Clearly explain the difference between external and internal respiration.
Problem 12
What is it about the structure of the alveoli that makes them an ideal site for gas exchange?
Problem 13
The contraction of the diaphragm and the external intercostal muscles begins inspiration. What happens, in terms of volume and pressure changes in the lungs, when these muscles contract?
Problem 19
As a result of a stroke, Mrs. Minnick's swallowing is uncoordinated. What detrimental effect might this have on her ability to breathe?