Back
BackProblem 1
The normal diploid number of human chromosomes is:
a. 48
b. 47
c. 46
d. 23
e. 24
Problem 2
Relative to differences between mitosis and meiosis, choose the statements that apply only to events of meiosis:
a. Tetrads present
b. Produces two daughter cells
c. Produces four daughter cells
d. Occurs throughout life
e. Reduces the chromosomal number by half
f. Synapsis and crossing over of homologous occur
Problem 3
The structures that draw an ovulated oocyte into the female duct system are:
a. Cilia
b. Fimbriae
c. Microvilli
d. Stereocilia
Problem 4
The usual site of embryo implantation is:
a. The uterine tube
b. The peritoneal cavity
c. The vagina
d. The uterus
Problem 5
Which of the following is correct relative to female anatomy?
a. The vaginal orifice is the most dorsal of the three openings in the perineum.
b. The urethra is between the vaginal orifice and the anus.
c. The anus is between the vaginal orifice and the urethra.
d. The urethra is the more ventral of the two orifices in the vulva.
Problem 6
Secondary sex characteristics are:
a. Present in the embryo
b. A result of male or female sex hormones increasing in amount at puberty
c. The testis in the male and the ovary in the female
d. Development of male and female external genitalia
Problem 7
Which of the following produces the male sex hormones?
a. Seminal glands
b. Corpus luteum
c. Developing follicles in the testes
d. Interstitial endocrine cells
Problem 8
Which will occur as a result of non-descent of the testes from the interior of the pelvis to the superficial scrotum?
a. Male sex hormones will not be circulated in the body.
b. Sperm will have no means of exit from the body.
c. Inadequate blood supply will retard the development of the testes.
d. Viable sperm will not be produced.
Problem 9
Match the key choices with the descriptive phrases below.
Key:
a. Androgen-binding protein
b. Estrogens
c. FSH
d. GnRH
e. Inhibin
f. LH
g. Progesterone
h. Testosterone
(1) Hormones that directly regulate the ovarian cycle
(2) Chemicals in males that inhibit the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis
(3) Hormone that makes the cervical mucus viscous
(4) Potentiates the activity of testosterone on spermatogenic cells
(5) Chemicals in females that inhibit the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis
(6) Stimulates the secretion of testosterone
Problem 10
Which of the following does not add a secretion that makes a major contribution to semen?
a. Prostate
b. Bulbo-urethral glands
c. Testes
d. Ductus deferens
Problem 11
The corpus luteum is formed at the site of:
a. Fertilization
b. Ovulation
c. Menstruation
d. Implantation
Problem 12
Sperm are to seminiferous tubules as oocytes are to:
a. Fimbriae
b. Corpus albicans
c. Ovarian follicles
d. Corpora lutea
Problem 13
FSH is to estrogens as high levels of estrogens are to:
a. Progesterone
b. LH
c. FSH
d. Testosterone
Problem 14
Why is the term urogenital system more applicable to males than to females?
Problem 15
Describe the major structural (and functional) regions of a sperm.
Problem 17
Define menarche. What does it indicate?
Problem 18
Trace the pathway of a sperm from the male testes to the uterine tube of a female.
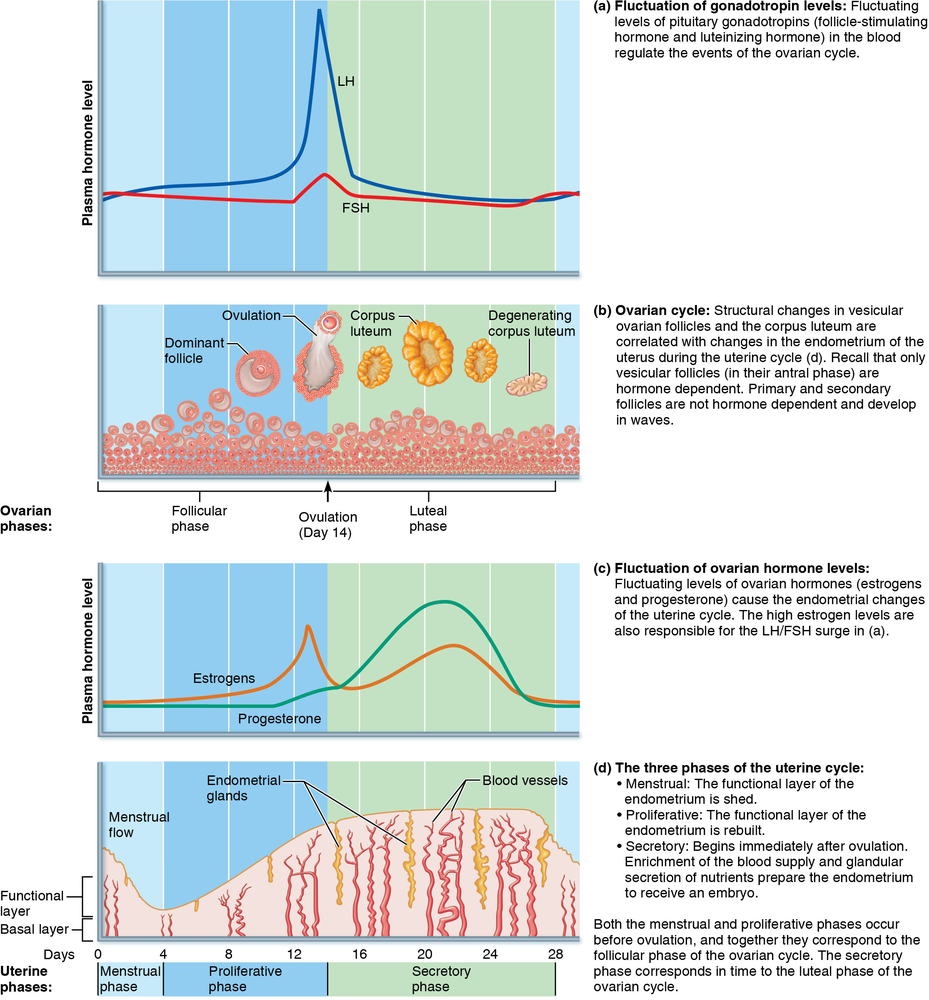
Problem 19
In menstruation, the functional layer is shed from the endometrium. Explain the hormonal and physical factors responsible for this shedding. (Hint: See Figure.)
Problem 20
Both the epithelium of the vagina and the cervical glands of the uterus help prevent the invasion and spread of vaginal pathogens. Explain how each of these mechanisms works.
Problem 21
Oogenesis in the female results in one functional gamete—the egg, or ovum. What other cells are produced? What is the significance of this rather wasteful type of gamete production—that is, production of a single functional gamete instead of four, as seen in males?
Problem 22
Gina Marciano, a 44-year-old mother of eight children, visited her physician complaining of a 'bearing down' sensation in her pelvis, low backache, and urinary incontinence. A vaginal examination showed that the external os of her cervix was just inside the vaginal orifice and her perineum exhibited large keloids (masses of scar tissue). What do you think Gina's problem is and what caused it? (Be anatomically specific.)
Problem 23
Grant, a sexually active adolescent, visited his doctor complaining of a red, painless swelling on his penis. He has no penile discharge or pain on urination. An account of his recent sexual behavior was requested and recorded.
a. What do you think Grant's problem is?
b. What is the causative agent of this disorder?
c. How is the condition treated, and what may happen if it isn't treated?
Problem 24
A 36-year-old mother of four is considering tubal ligation to ensure that her family gets no larger. She asks the physician if she will become 'menopausal' after the surgery.
a. How would you answer her question and explain away her concerns?
b. Explain what a tubal ligation is.
Problem 26
Erin had both her left ovary and her right uterine tube removed surgically at age 17 because of a cyst and a tumor in these organs. Now, at age 32, she remains healthy and is expecting her second child. How could Erin conceive a child with just one ovary and one uterine tube, widely separated on opposite sides of the pelvis like this?