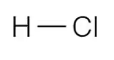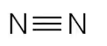Back
BackProblem 2
All of the following are examples of the four major elements contributing to body mass except:
a. Hydrogen
b. Carbon
c. Nitrogen
d. Sodium
e. Oxygen
Problem 3
The subatomic particles responsible for the chemical behavior of atoms are
(a) Electrons
(b) Ions
(c) Neutrons
(d) Protons
Problem 4
Which of the following does not describe a mixture?
a. Properties of its components are retained
b. Chemical bonds are formed
c. Components can be separated physically
d. Includes both heterogeneous and homogeneous examples
Problem 5
In a beaker of water, the water-water bonds can properly be called:
a. Ionic bonds
b. Polar covalent bonds
c. Nonpolar covalent bonds
d. Hydrogen bonds
Problem 6
When a pair of electrons is shared between two atoms, the bond formed is called:
a. A single covalent bond
b. A double covalent bond
c. A triple covalent bond
d. An ionic bond
Problem 7
Factors that accelerate the rate of chemical reactions include all but:
a. The presence of catalysts
b. Increasing the temperature
c. Increasing the particle size
d. Increasing the concentration of the reactants
Problem 8
Which of the following molecules is an inorganic molecule?
a. Sucrose
b. Cholesterol
c. Collagen
d. Sodium chloride
Problem 9
Acids:
a. Release hydroxyl ions when dissolved in water
b. Are proton acceptors
c. Cause the pH of a solution to rise
d. Release protons when dissolved in water
Problem 10
A triglyceride consists of:
a. Glycerol plus three fatty acids
b. A sugar-phosphate backbone to which two amino groups are attached
c. Two to several hexoses
d. Amino acids that have been thoroughly saturated with hydrogen
Problem 11
The lipid(s) used as the basis of vitamin D, sex hormones, and bile salts is/are:
a. Triglycerides
b. Cholesterol
c. Phospholipids
d. Prostaglandin
Problem 12
Provide the atomic symbol for each of the following elements:
a. Calcium
b. Carbon
c. Hydrogen
d. Iron
Problem 12b
Provide the atomic symbol for each of the following elements:
e. Nitrogen
f. Oxygen
g. Potassium
h. Sodium
Problem 13
A deficiency in this element can be expected to reduce the hemoglobin content of blood:
a. Fe
b. I
c. F
d. Ca
e. K
Problem 14
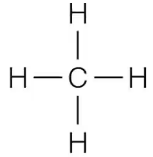
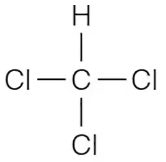
Which of the following covalently bonded molecules are polar?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Problem 15
Identify each reaction as one of the following:
a. A synthesis reaction
b. A decomposition reaction
c. An exchange reaction
(1) 2Hg + O₂ → 2HgO
(2) HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O
Problem 16
A chemist, during the course of an analysis, runs across a chemical composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in the proportion 1:2:1 and having a six-sided molecular shape. It is probably:
a. A pentose
b. An amino acid
c. A fatty acid
d. A monosaccharide
e. A nucleic acid
Problem 17
How many moles of aspirin, C₉H₈O₄, are in a bottle containing 450 g by weight? (Note: The approximate atomic weights of its atoms are C = 12, H = 1, and O = 16.)
Problem 19
Consider the following information about three atoms: 12/6 C 13/6 C 14/6 C
a. How are they similar to one another?
b. How do they differ from one another?
c. What are the members of such a group of atoms called?
d. Using the planetary model, draw the atomic configuration of 12/6 C, showing the relative position and numbers of its subatomic particles
Problem 20
What are hydrogen bonds and how are they important in the body?
Problem 21
Differentiate clearly between primary, secondary, and tertiary protein structure.
Problem 23
Explain why, if you pour water into a glass very carefully, you can 'stack' the water slightly above the rim of the glass.
Problem 24
Some antibiotics act by binding to certain essential enzymes in the target bacteria.
a. How might these antibiotics influence the chemical reactions controlled by the enzymes?
b. What is the anticipated effect on the bacteria? On the person taking the antibiotic prescription?
Problem 25
Mrs. Roberts, in a diabetic coma, has just been admitted to Noble Hospital. Her blood pH indicates that she is in severe acidosis (low blood pH), and measures are quickly instituted to bring her blood pH back within normal limits.
a. Define pH and note the normal pH of blood.
b. Why is severe acidosis a problem?
Problem 26
Jason, a 12-year-old boy, was awakened suddenly by a loud crash. As he sat up in bed, straining to listen, his fright was revealed by his rapid breathing (hyperventilation), a breathing pattern effective in ridding the blood of CO₂. At this point, was his blood pH rising or falling?
Problem 27
After you eat a protein bar, which chemical reactions introduced in this chapter must occur for the amino acids in the protein bar to be converted into proteins in your body cells?