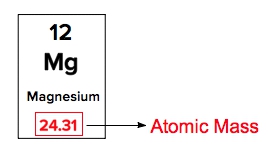
Atomic masses of elements are readily available on the periodic table, where each element is represented by a symbol, such as H for hydrogen. The whole numbers associated with each element indicate their atomic number, which corresponds to the number of protons in the nucleus. In contrast, atomic mass is typically not a whole number; it represents the weighted average of all isotopes of an element.
The atomic mass is expressed in units of grams per mole, atomic mass units (AMU), or Daltons. A key relationship to remember is that 1 AMU is equivalent to \(1.66 \times 10^{-27}\) kilograms. This means that the atomic masses listed on the periodic table reflect the average of all isotopes for each element, rather than a single fixed value. It is important to note that only the heaviest elements tend to have whole number atomic masses, while lighter elements usually display decimal values.