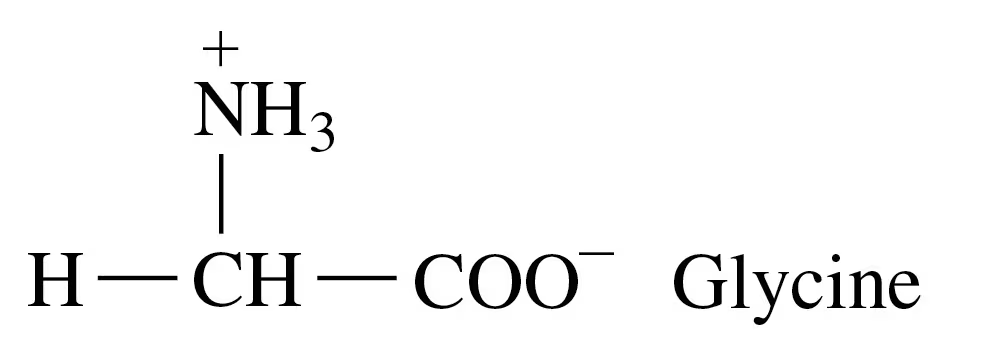Back
BackProblem 17
What coenzyme picks up hydrogen when a carbon–carbon double bond is formed?
Problem 21
How is ATP used in the initial steps of glycolysis?
Problem 27a
How many ATP or NADH are produced (or required) in each of the following steps in glycolysis?
a. glucose to glucose-6-phosphate
Problem 28b
How many ATP or NADH are produced (or required) in each of the following steps in glycolysis?
c. phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate
Problem 30
What coenzymes are needed for the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA?
Problem 33
How does the formation of lactate permit glycolysis to continue under anaerobic conditions?
Problem 35
What are the products from one turn of the citric acid cycle?
Problem 37a
Identify the reaction(s) of the citric acid cycle that involve(s)
a. oxidation and decarboxylation
Problem 38b
Identify the reaction(s) of the citric acid cycle that involve(s)
c. hydration
Problem 40
What is the total NADH and total FADH2 produced in one turn of the citric acid cycle?
Problem 41b
Refer to the diagram of the citric acid cycle in Figure 18.13 to answer each of the following:
b. How is the number of carbon atoms decreased?
Problem 41d
Refer to the diagram of the citric acid cycle in Figure 18.13 to answer each of the following:
d. What are the decarboxylation reactions?
Problem 42b
Refer to the diagram of the citric acid cycle in Figure 18.13 to answer each of the following:
b. What are the four-carbon compounds?
Problem 42d
Refer to the diagram of the citric acid cycle in Figure 18.13 to answer each of the following:
d. In which reactions are secondary alcohols oxidized?
Problem 44
What happens to the energy level as electrons are passed along in electron transport?
Problem 47
Where is NADH oxidized in electron transport, and what is its oxidized form?
Problem 50
How is the H+ gradient established?
Problem 53
How are glycolysis and the citric acid cycle linked to the production of ATP by electron transport?
Problem 55a
What is the ATP energy yield associated with each of the following?
a. NADH → NAD+
Problem 55b
What is the ATP energy yield associated with each of the following?
c. 2 pyruvate → 2 acetyl CoA + 2CO2
Problem 56a
What is the ATP energy yield associated with each of the following?
a. FADH2 → FAD
Problem 57a
Caprylic acid, CH3 ― (CH2)6 ― COOH, is a C8 fatty acid found in milk.
a. State the number of β oxidation cycles for the complete oxidation of caprylic acid.
Problem 58a
Lignoceric acid, CH3 ― (CH2)22 ― COOH, is a C24 fatty acid found in peanut oil in small amounts.
a. State the number of β oxidation cycles for the complete oxidation of lignoceric acid.
Problem 59a
Consider the complete oxidation of oleic acid, CH3 ― (CH2)7 ― CH = CH ― (CH2)7 ― COOH, which is a C18 monounsaturated fatty acid.
a. How many cycles of β oxidation are needed?
Problem 60a
Consider the complete oxidation of palmitoleic acid, CH3 ― (CH2)5 ― CH = CH ― (CH2)7 ― COOH, which is a C16 monounsaturated fatty acid found in animal and vegetable oils..
a. How many cycles of β oxidation are needed?
Problem 63
What are some conditions that characterize ketosis?
Problem 65b
Draw the condensed structural formula for the α-keto acid produced from each of the following in transamination:
a.
Problem 67
Why does the body convert NH4+ to urea?
Problem 68
Draw the condensed structural formula for urea.
Problem 69c
What metabolic substrate(s) are produced from the carbon atoms of each of the following amino acids?
c. tyrosine