Textbook Question
Identify each pathway as anabolic or catabolic
b. citric acid cycle

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Identify each pathway as anabolic or catabolic
b. citric acid cycle
Identify each pathway as anabolic or catabolic.
a. gluconeogenesis
Identify the type of food—carbohydrate, fat, or protein—that gives each of the following digestion products:
b. fatty acid
How and where does sucrose undergo digestion in the body? Name the products.
If glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm and the citric acid cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix, how do the products of glycolysis get inside the mitochondrial matrix?
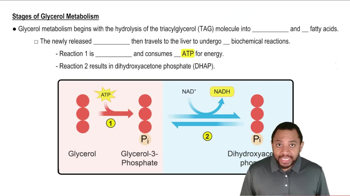
Which of the following reactions in glycolysis produce ATP or NADH?
a. 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to 3-phosphoglycerate